A Brief Introduction To 3D Printing for Architectural Models creation
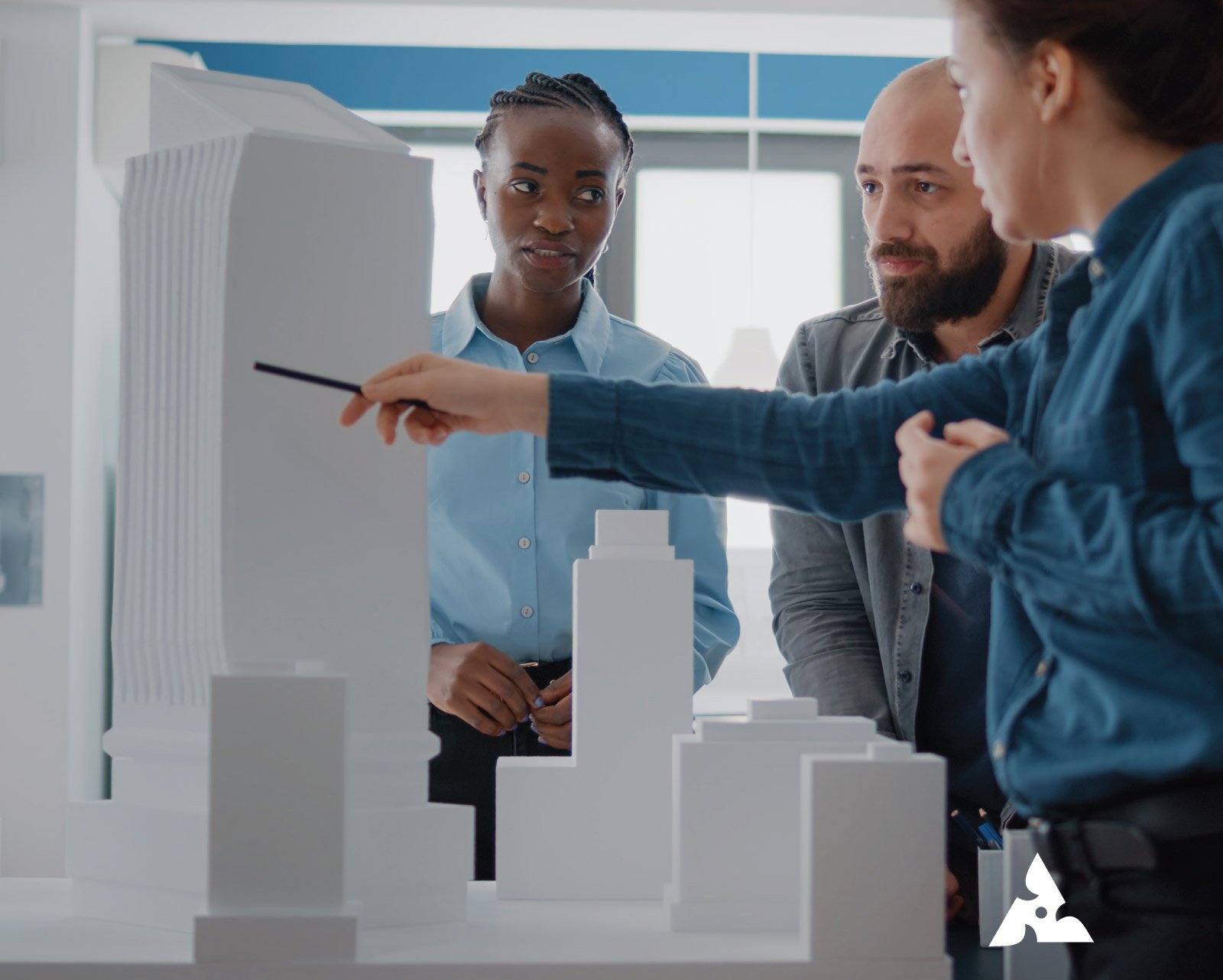
3D printing is a revolutionary technology that has been gaining popularity in recent years, especially in the field of architectural model making. It offers architects and designers the ability to create highly accurate, detailed and intricate models that were previously impossible to produce with traditional methods.
In this article, we will provide a basic introduction to 3D printing for architectural model making, covering the basics of the technology, the benefits it offers, and some of the key considerations when using 3D printing for architectural models.
What is 3D Printing?
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a process that involves the creation of three-dimensional objects from a digital file. The process involves building the object layer by layer, using a range of materials including plastic, metal, and even food.
3D printing has rapidly advanced since its inception and has become an important tool for product development, prototyping, and manufacturing. In architecture, 3D printing is now being used to create highly detailed and accurate models of buildings and structures.
Types of Technology in 3D Printing Model
There are several types of 3D printing technologies, each with their unique advantages and limitations. Here are some of the most common types:
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) – This is the most common type of 3D printing technology, where a thermoplastic filament is melted and extruded layer by layer to create the 3D model.
- Stereolithography (SLA) – This technology uses a liquid resin that is cured with UV light layer by layer to create the 3D model.
- Digital Light Processing (DLP) – Similar to SLA, DLP uses a liquid resin that is cured with UV light, but instead of a laser, a digital light projector is used to cure the resin.
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) – In this technology, a laser selectively sinters (melts and fuses) powdered material layer by layer to create the 3D model.
- Binder Jetting – This technology uses a liquid binder to selectively bond powder particles layer by layer to create the 3D model.
- Material Jetting – This technology uses inkjet printhead technology to jet small droplets of material onto a build tray layer by layer to create the 3D model.
- Electron Beam Melting (EBM) – This technology uses an electron beam to melt and fuse metal powder layer by layer to create the 3D model.
Each technology has its strengths and weaknesses, and choosing the right technology depends on the specific requirements of the project.
Benefits of 3D Printing for Architectural Model Making
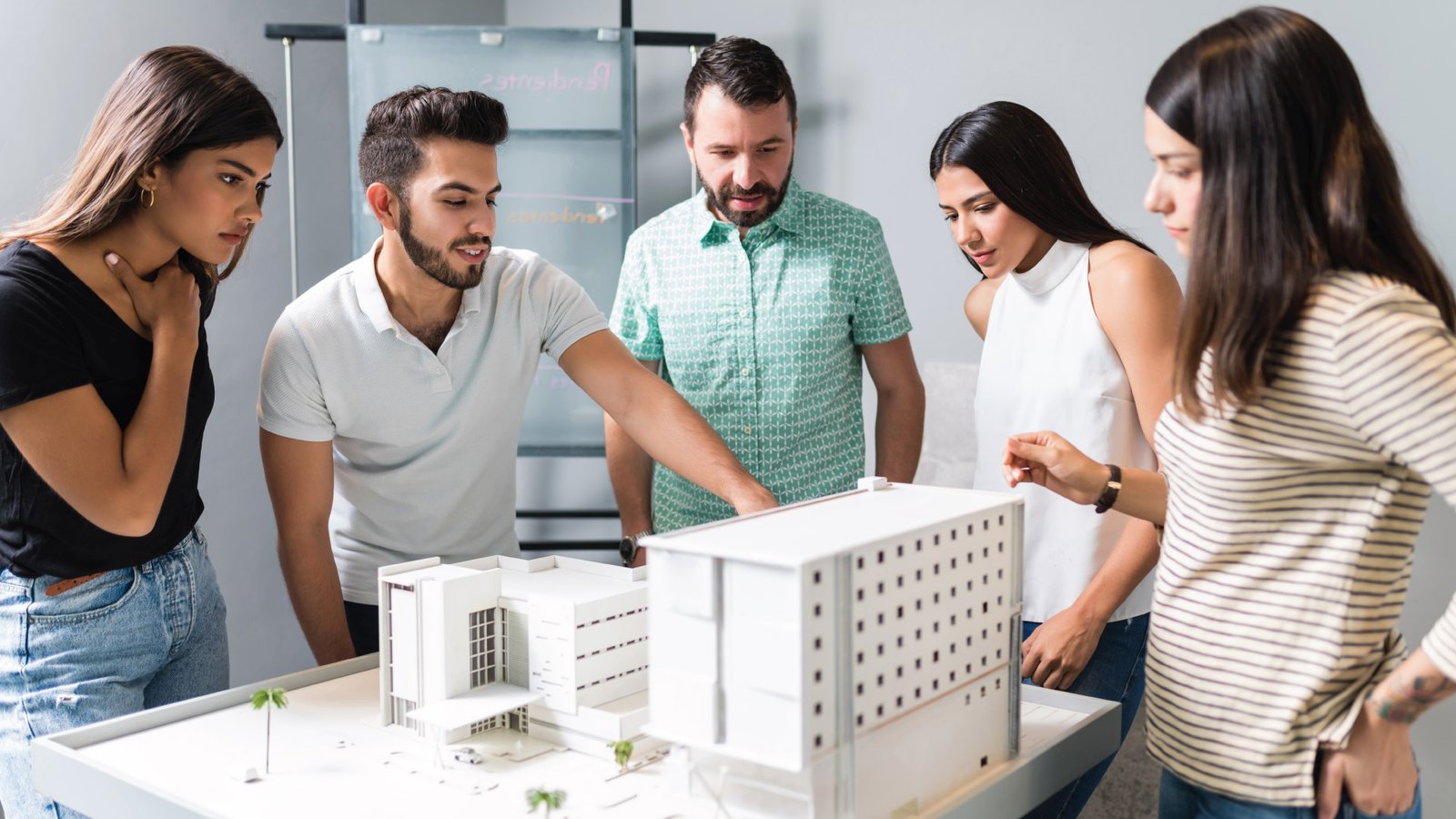
One of the primary benefits of 3D printing for architectural model making is its ability to produce highly detailed and complex models with ease. Traditional model-making methods such as hand carving, molding, and casting can be time-consuming and expensive, especially for intricate designs.
3D printing can also help architects and designers to quickly produce multiple iterations of a model, allowing for quick and easy design changes. This is particularly useful for projects that require rapid prototyping and testing.
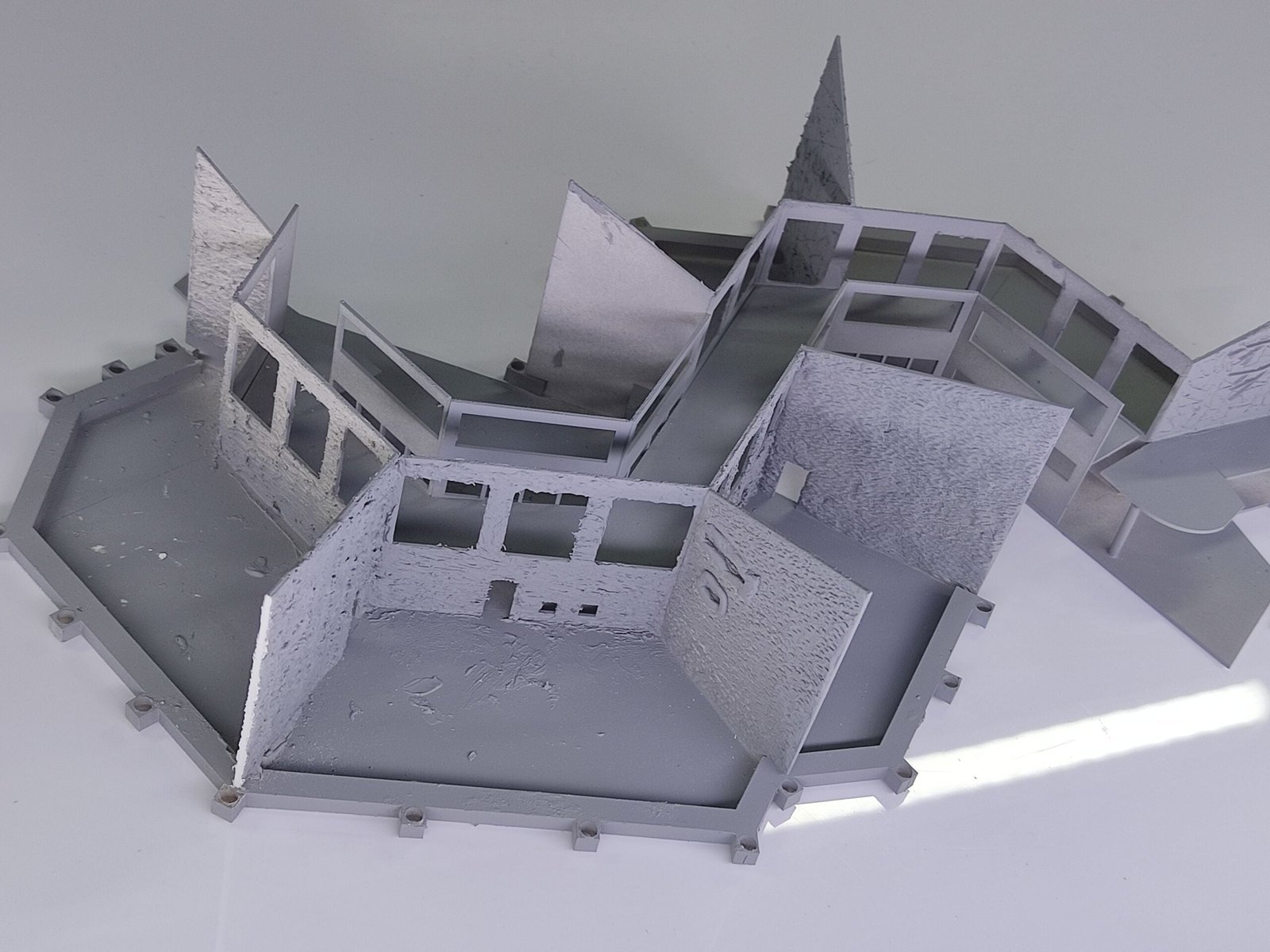
Another key benefit of 3D printing for architectural model making is the ability to create models that accurately reflect the final building or structure. This is achieved through the use of digital modeling software that allows designers to create detailed models with precise measurements.
Key Considerations When Using 3D Printing for Architectural Models
When using 3D printing for architectural model making, there are several key considerations that architects and designers should keep in mind:
- Scale: Ensure that the scale of the model accurately reflects the final building or structure.
- Material selection: Choose the appropriate material for the model based on the desired level of detail and finish.
- Printing orientation: Consider the orientation of the model during printing to ensure optimal strength and accuracy.
- Support structures: Support structures may be necessary to ensure that the model prints correctly.
- Post-processing: Depending on the chosen material, post-processing may be necessary to achieve the desired finish.
3D printing is a powerful technology that is changing the way architects and designers approach model making. Its ability to quickly produce highly accurate and detailed models makes it an attractive option for architectural model making.
By considering the key considerations outlined in this article, architects and designers can ensure that they get the most out of 3D printing when creating their models.