Master Plan Model Making
Architectural Master Plan Model Makers / City Miniature Model Makers /
Prototyping/ Urban city Planning Model
Practice safe design: Use a concept. – Petrula Vrontikis
“The best way to predict the future is to create it.”
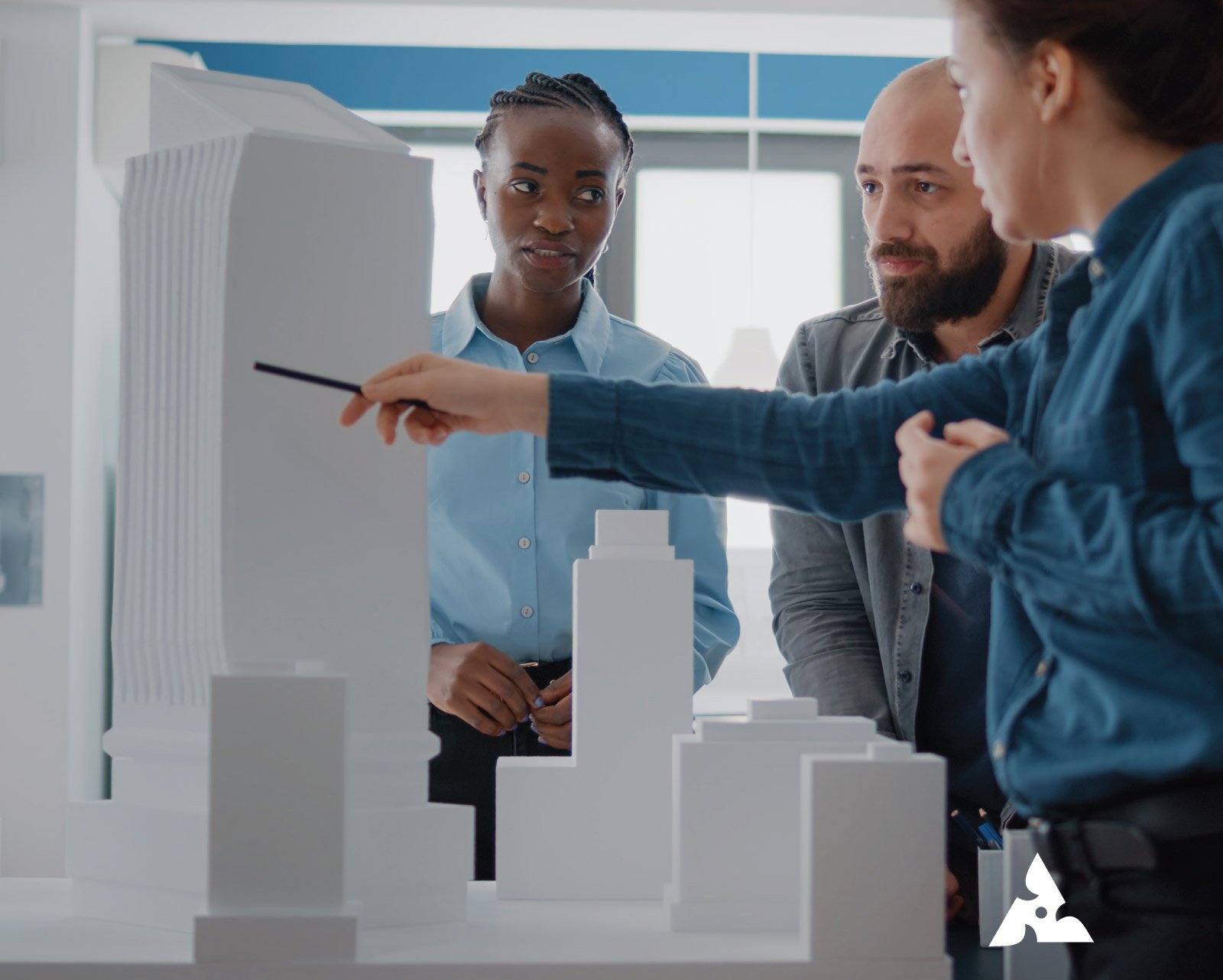
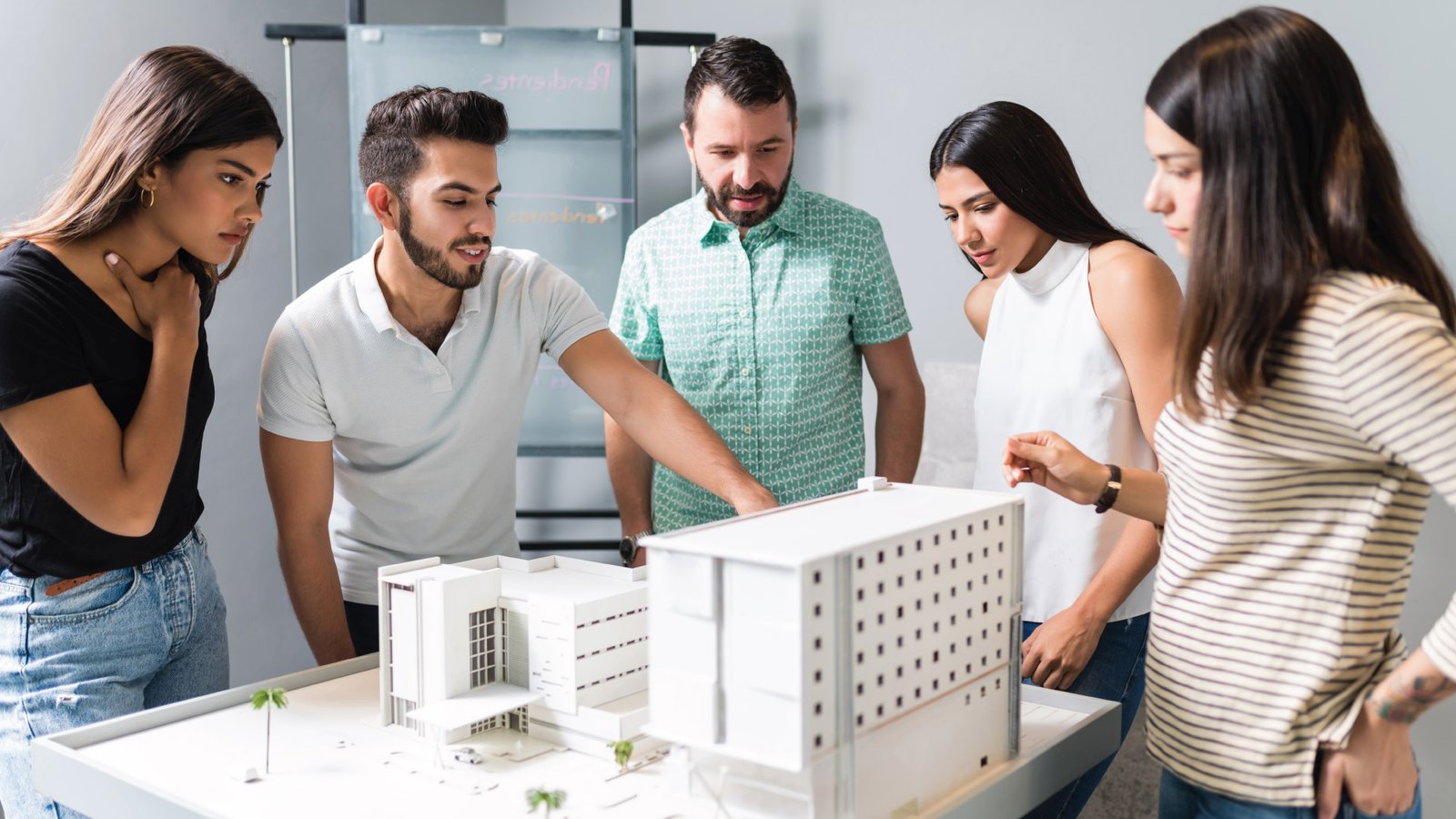
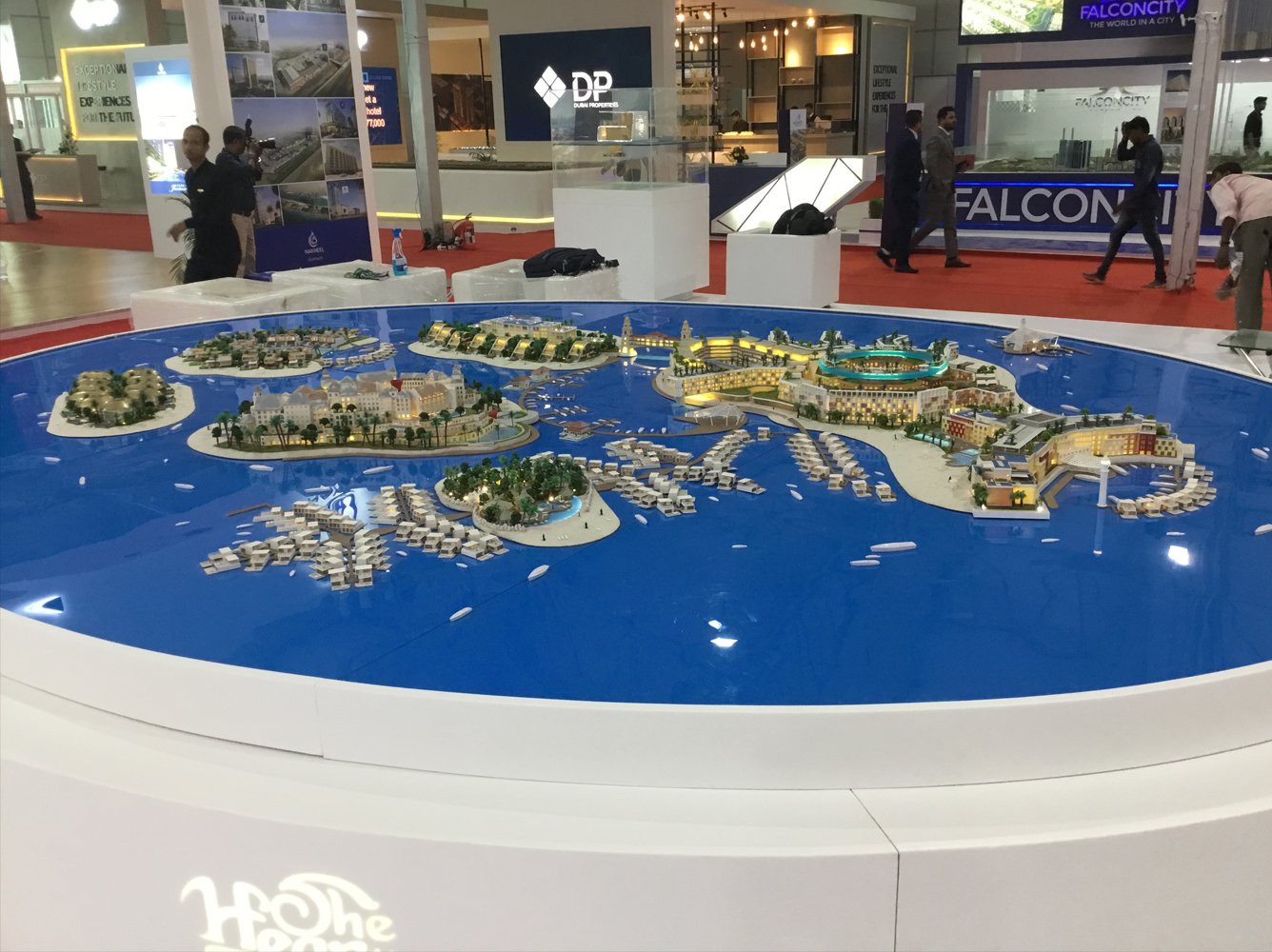
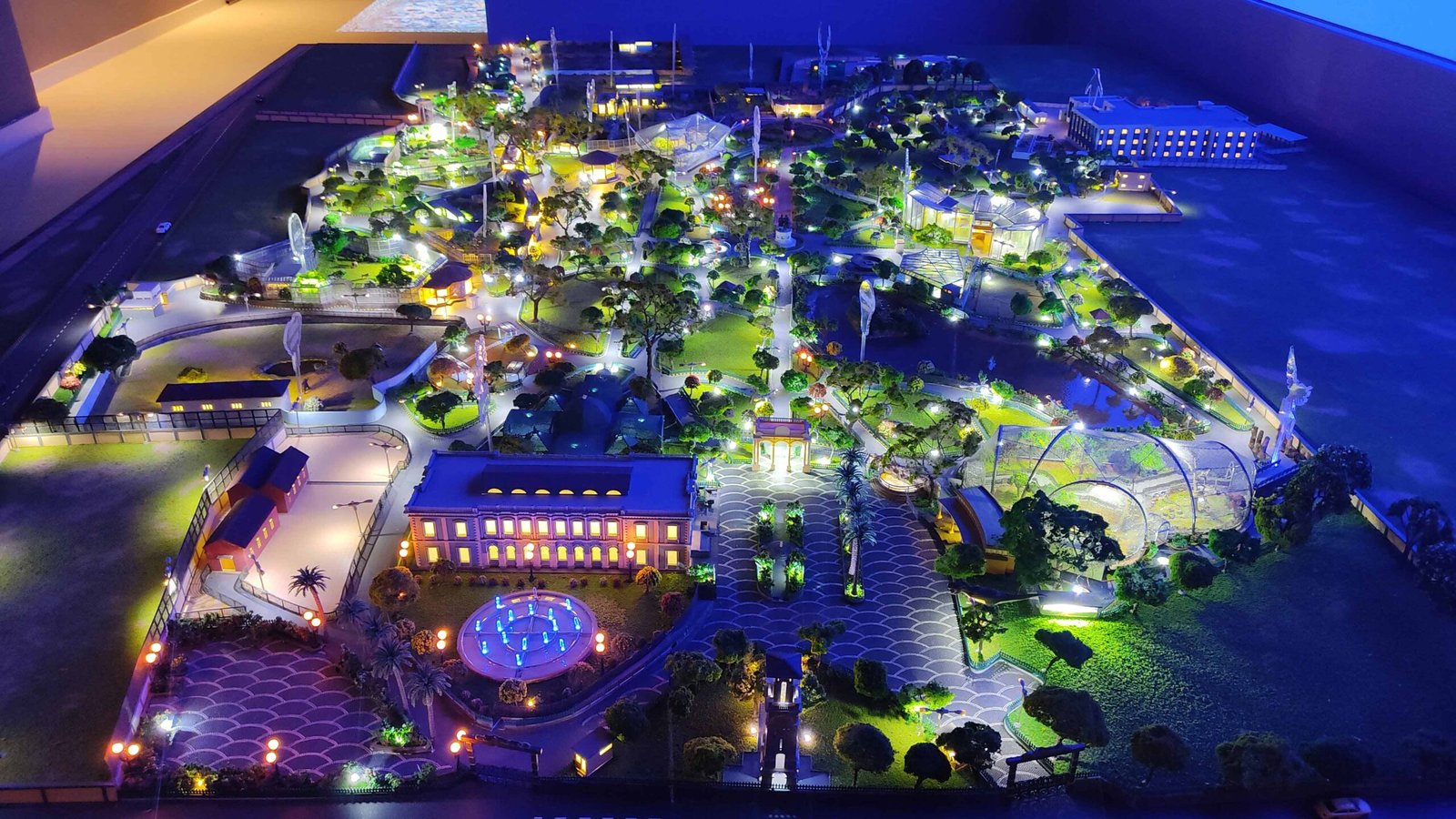
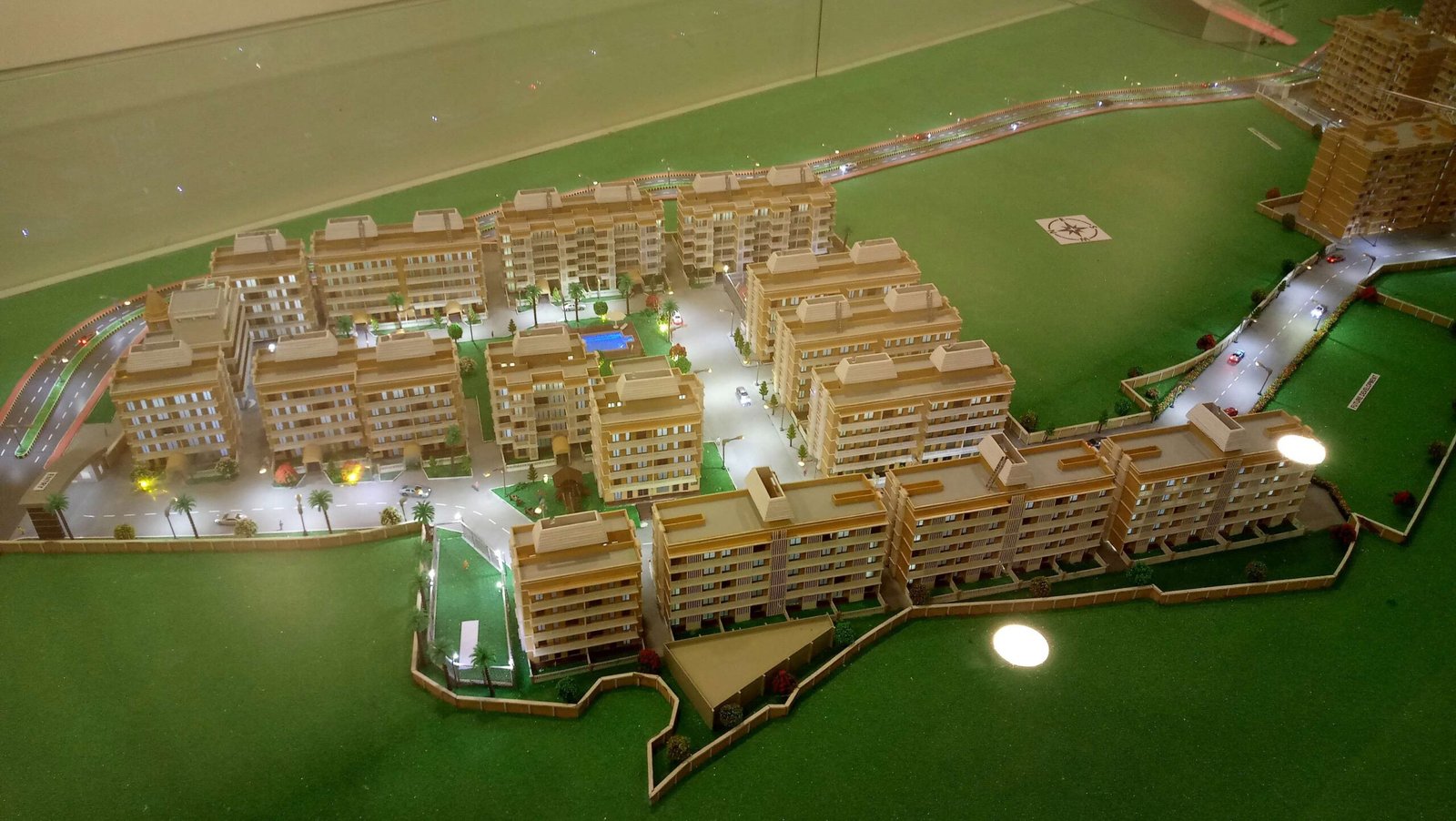
Conceptual masterplan models visually outline the design and layout of projects in urban planning, architecture, and landscape design. They represent comprehensive plans for large areas like city districts. These models are crucial tools for articulating and visualizing planned development, facilitating communication and decision-making among stakeholders.
Masterplan Models Portfolio
FAQ's
If this is your first time seeking an master plan scale model-making service, you likely have some questions. Read on to learn more!
A master plan scale model is a detailed, scaled-down replica of a proposed development or architectural project, such as urban planning, landscape design, or large building projects. It represents the overall layout, design, and spatial relationships of the project to help visualize and communicate the final outcome. These models often include buildings, roads, green spaces, and other key features, and are used for planning, presentations, and public consultations. The scale allows stakeholders to understand the project’s scope and how it fits within its environment.
– 1:1000: This scale is often used for larger areas or urban planning projects, providing a broad overview of the layout and spatial relationships.
– 1:500: This scale offers more detail and is suitable for smaller sites or where more intricate design features need to be represented clearly.
The choice of scale depends on the project’s size, the level of detail required, and the purpose of the model. For very large projects or public presentations, larger scales might be preferred to convey more detail.
1. Conceptualization: Define the project’s scope, objectives, and key elements. Gather all relevant data, including site plans, architectural drawings, and design concepts.
2. Design and Planning: Create detailed plans and drawings of the master plan, including all structures, roads, green spaces, and other features. Determine the appropriate scale for the model.
3. Material Selection: Choose materials for the model based on the level of detail required and the intended presentation. Common materials include foam board, acrylic, wood, and plastic.
4. Base Construction: Build the base of the model to represent the terrain and overall layout. This might involve carving or shaping materials to match the topography.
5. Model Building: Construct the individual components of the model, such as buildings, roads, and landscaping. Use precise measurements to ensure accuracy and scale.
6. Detailing: Add fine details such as textures, colors, and small features to enhance realism. This might include painting, adding miniature trees, or placing model figures.
7. Assembly: Assemble the various parts of the model onto the base, ensuring that all elements fit together correctly and align with the master plan.
8. Review and Refinement: Inspect the model for accuracy and make any necessary adjustments. Ensure that it effectively represents the master plan and meets the project’s objectives.
9. Presentation: Prepare the model for display or presentation, including mounting it on a suitable base or stand and providing any additional information or context for viewers.
This process ensures that the master plan model accurately reflects the proposed project and effectively communicates its design and layout.
1. Conceptual Models: Provide a broad overview of the project, focusing on general layout and major elements. Scales often range from 1:1000 to 1:2000.
2. Detailed Models: Show more intricate details of specific areas or components of the master plan. Scales typically range from 1:500 to 1:1000.
3. Architectural Models: Focus on specific buildings or structures within the master plan, highlighting architectural details. Scales often range from 1:100 to 1:200.
4. Landscape Models: Emphasize the surrounding landscape and how it integrates with the built environment. Scales can vary widely, commonly 1:500 to 1:1000.
5. Environmental Models: Include elements such as green spaces, water features, and ecological systems, often at scales similar to detailed or landscape models.
Each type of model serves a different purpose, from providing an overall view to showcasing specific elements in detail.
LET'S CONNECT !!!
Contact Maadhu creatives & We’re here to help you grow your business.