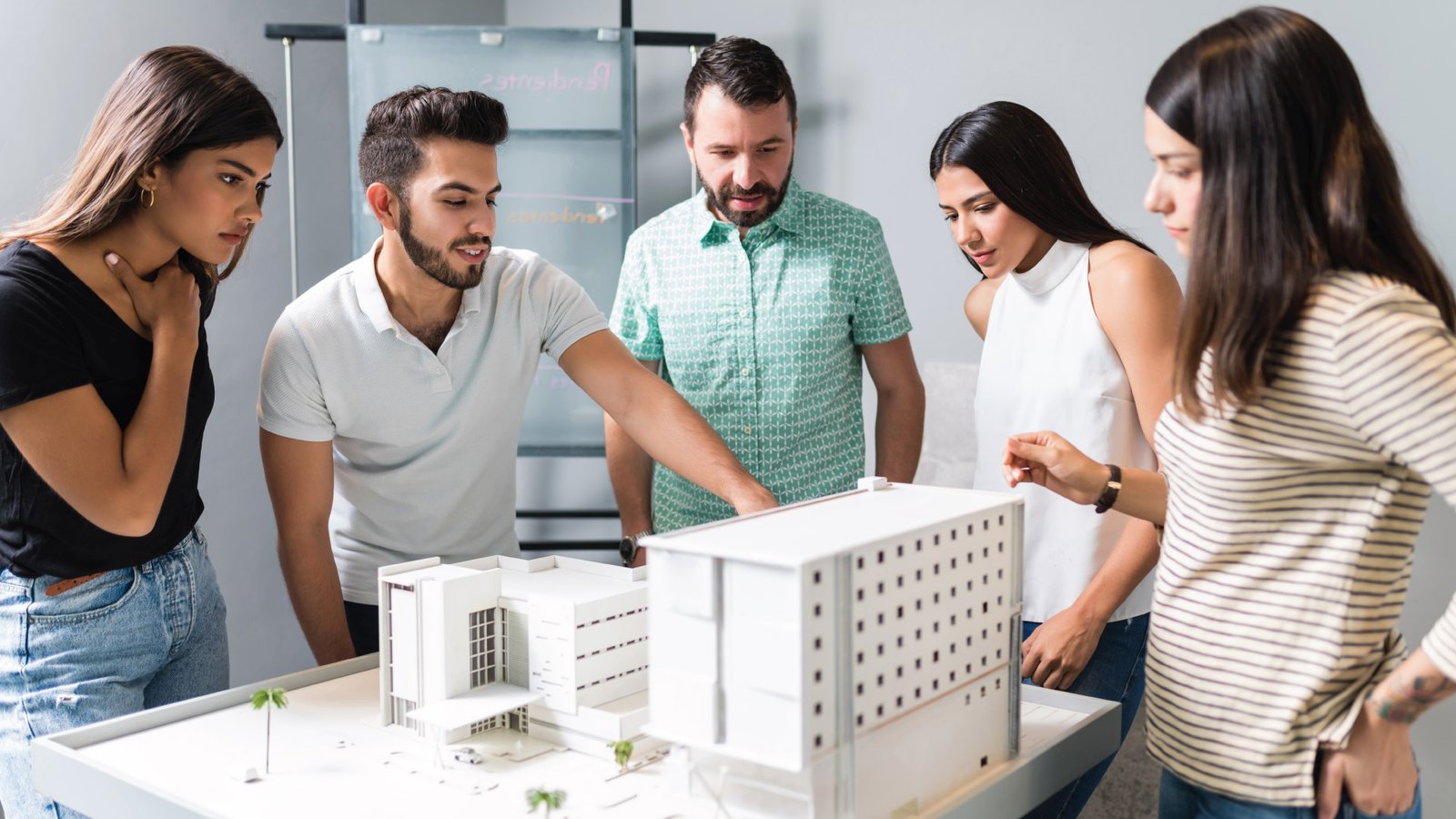
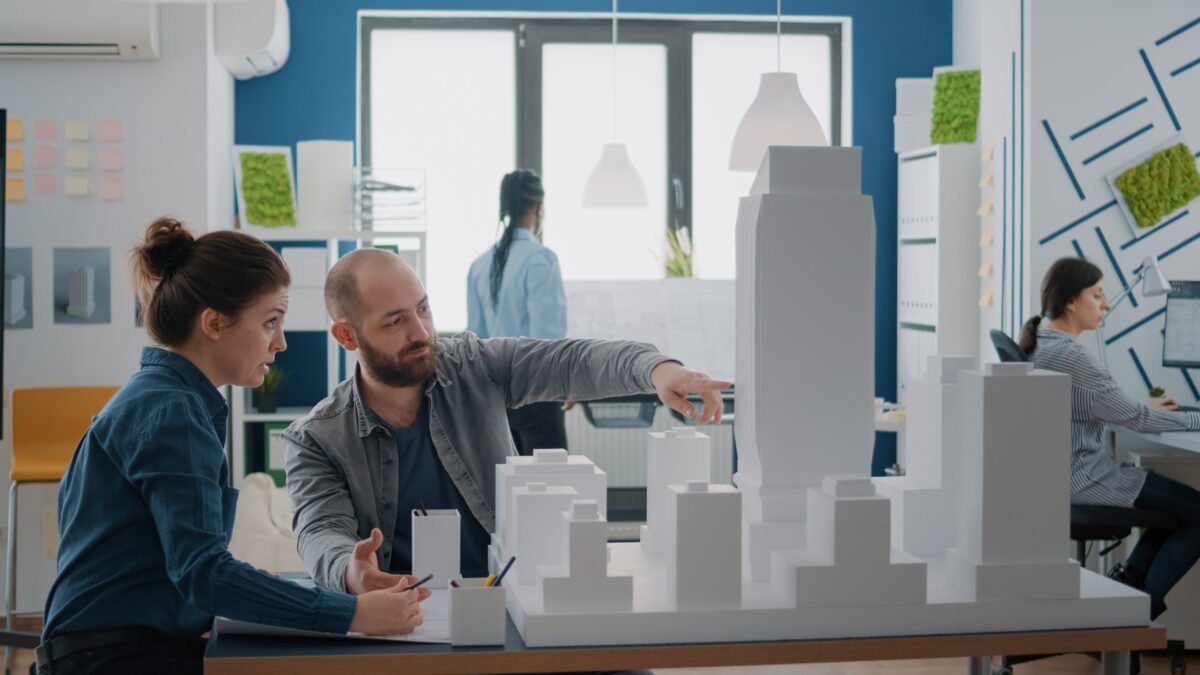
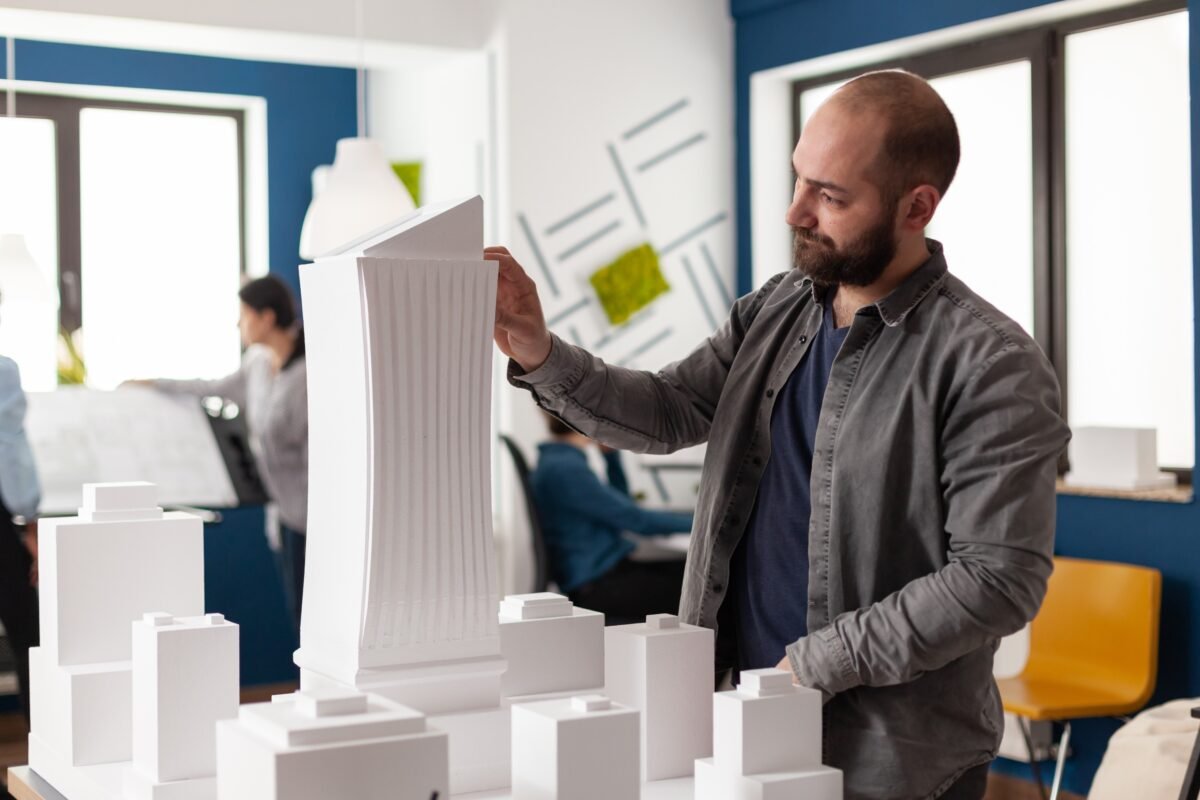
Architectural Model Maker Jobs in India Introduction to Architectural Model Maker Jobs Architectural model makers play a crucial role in the construction and design industry, bringing architectural visions to life through intricate scale models. In India, the demand for skilled model makers is on the rise, with various architectural firms, real estate developers, and engineering consultancies seeking their expertise. What Does an Architectural Model Maker Do? Creating Scale Models One of the primary responsibilities of an architectural model maker is to create accurate scale models of buildings and structures based on architectural blueprints and designs. These models serve as visual representations, helping architects, designers, and clients better understand the spatial layout and aesthetics of a project. Using Various Materials Model makers utilize a wide range of materials such as wood, plastic, foam, and clay to construct detailed models. Each material has its own advantages and is chosen based on the specific requirements of the project. For example, foam is often used for its lightweight properties, while wood provides durability and stability. Collaborating with Architects and Designers Architectural model makers work closely with architects, designers, and other professionals throughout the model-making process. They interpret design concepts, provide input on materials and techniques, and ensure that the final model accurately reflects the intended vision of the project. Skills Required for Architectural Model Maker Jobs Attention to Detail Precision and attention to detail are essential qualities for architectural model makers. They must meticulously replicate every aspect of a building, from the facade details to interior furnishings, ensuring that the model is an accurate representation of the final structure. Creativity and Innovation While accuracy is important, model makers also need to be creative and innovative in their approach. They may encounter challenges during the construction process and must be able to problem-solve and adapt their techniques to achieve the desired outcome. Technical Skills Proficiency in various technical skills such as carpentry, 3D modeling software, and model-making techniques is crucial for success in this profession. Model makers must have a strong understanding of geometry, scale, and spatial relationships to create realistic and visually appealing models. Education and Training Architectural Background Many architectural model makers have a background in architecture or a related field, providing them with a solid understanding of architectural principles and design concepts. However, formal education is not always a requirement, and individuals with a passion for model making can develop their skills through alternative means. Model Making Courses There are several specialized courses and workshops available for aspiring model makers, covering topics such as model construction techniques, material selection, and digital modeling software. These programs provide hands-on training and valuable industry insights to help individuals kickstart their careers in model making. On-the-Job Training Many architectural firms and model making studios offer on-the-job training programs for entry-level model makers. These opportunities allow individuals to gain practical experience, refine their skills, and learn from experienced professionals in the field. Job Opportunities in India Architectural Firms Architectural firms are among the primary employers of architectural model makers in India. They rely on model makers to create detailed representations of their architectural designs, which are used for presentations, client meetings, and project development. Real Estate Developers Real estate developers often require scale models to showcase their proposed developments to potential investors, buyers, and stakeholders. Model makers play a crucial role in helping developers visualize and communicate their project ideas effectively. Engineering Consultancies Engineering consultancies involved in infrastructure projects such as bridges, highways, and urban planning also hire architectural model makers. These models help engineers and planners assess design concepts, analyze spatial relationships, and identify potential challenges before construction begins. Salary Expectations Entry-level Salaries Entry-level architectural model makers in India can expect to earn salaries ranging from INR 15,000 to INR 25,000 per month, depending on factors such as education, skills, and location. Experienced Model Makers Experienced model makers with several years of experience and a strong portfolio can command higher salaries, ranging from INR 30,000 to INR 50,000 per month or more. Factors Affecting Salaries Salaries for architectural model makers may vary based on factors such as the size and reputation of the employer, the complexity of the projects, and the individual’s level of expertise and specialization. Challenges and Rewards Precision and Accuracy One of the biggest challenges faced by architectural model makers is achieving precision and accuracy in their models. They must meticulously measure and cut materials, ensuring that every detail is faithfully replicated according to the design specifications. Satisfaction of Seeing Projects Come to Life Despite the challenges, architectural model makers find immense satisfaction in seeing their projects come to life. The ability to transform architectural concepts into tangible models that inspire and impress clients is a rewarding aspect of the job. Competition in the Industry The architectural model making industry in India is highly competitive, with many talented professionals vying for opportunities. Model makers must continuously hone their skills, stay updated on industry trends, and differentiate themselves to succeed in this competitive landscape. Future Prospects Technological Advancements Advancements in technology such as 3D printing, laser cutting, and digital modeling software are transforming the field of architectural model making. Model makers who embrace these technologies can enhance their efficiency, accuracy, and creativity in model construction. Diversification of Projects As India continues to undergo rapid urbanization and infrastructure development, the demand for architectural model makers is expected to grow. Model makers may have the opportunity to work on diverse projects ranging from commercial complexes and residential towers to public infrastructure and cultural institutions. Sustainability and Environmental Concerns With increasing awareness of environmental sustainability, architectural model makers are also embracing eco-friendly practices in their craft. They are exploring renewable materials, recyclable options, and energy-efficient processes to minimize the environmental impact of model making. Tips for Aspiring Model Makers Continuous Learning To excel in the field of architectural model making, aspiring model makers should pursue continuous learning opportunities. They can attend workshops, seminars, and online courses to stay updated on the latest techniques, materials, and technologies.