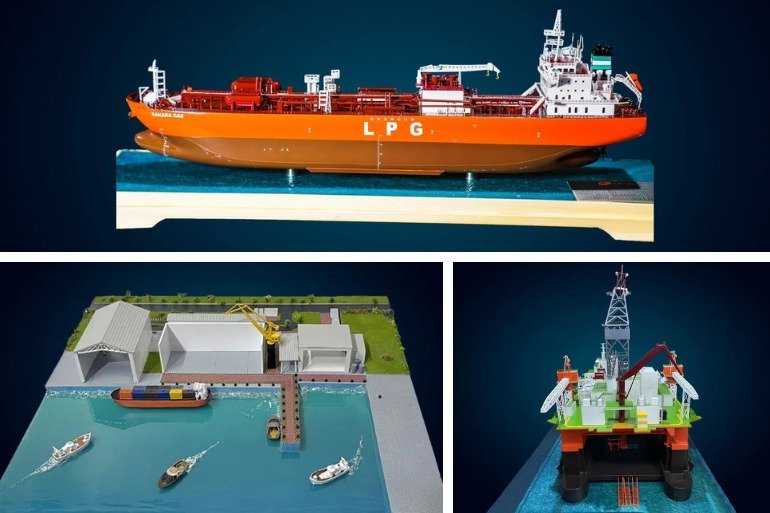
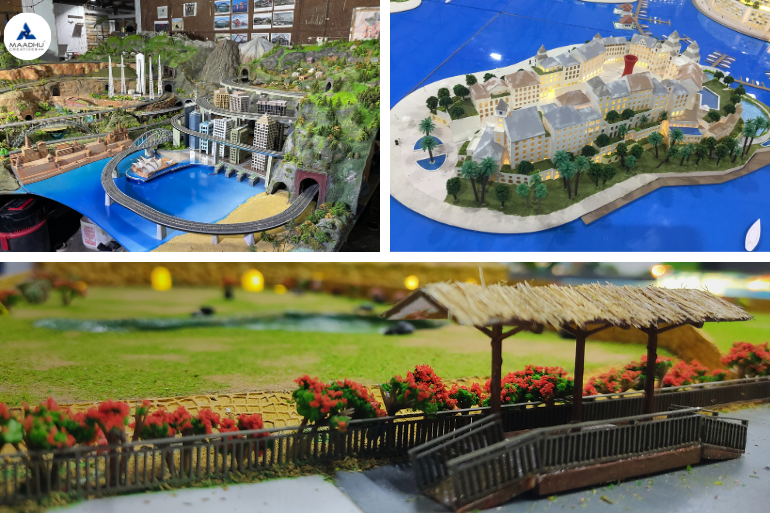
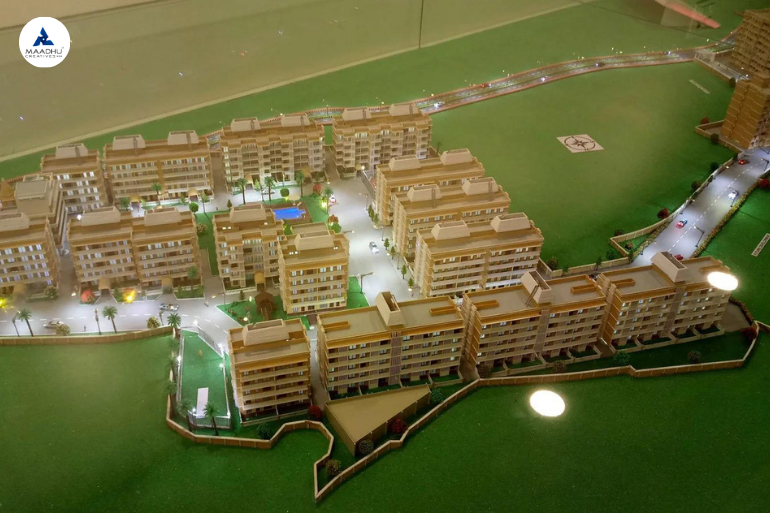
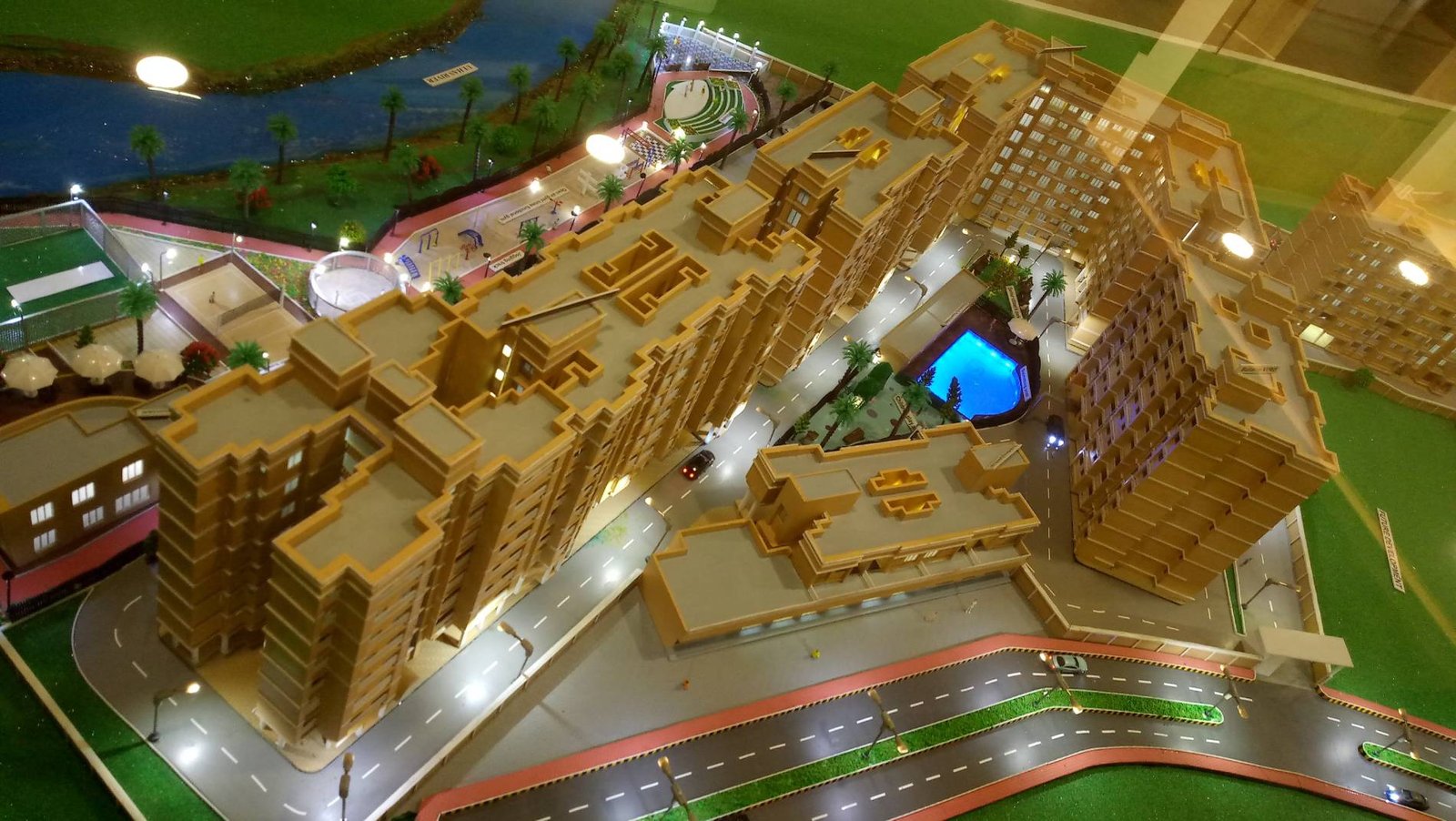
Marine Model Making Process: An In-Depth Guide by Maadhu Creatives Table of Contents Marine model-making is a craft that brings to form the grandiosity of ships and marine vessels in the small and detailed hands. The blend of engineering precision with an artistic flair brings to life not only historical and contemporary vessels but also serves educational, design, and preservation purposes. Maadhu Creatives specializes in the creation of high-quality, complete marine models reflecting artistry and technical expertise. This very inclusive guide will take us through the meaning and relevance of marine models, the process of model making, and also how you will be able to make your very own. Meaning of Marine Model Marine models are physical copies of ships, boats, and various marine vessels but in smaller sizes than the original. These models hold significant value across various sectors:These models hold significant value across various sectors: Educational Tools: Marine models are models that are used in order to teach people more about the area of naval engineering including naval architecture, ship construction, and marine engineering. They assist students and enthusiasts of ship design and engineering to appreciate some of the most technical aspects that are involved in construction and operation of ships by pointing towards these examples. Design Verification: In addition to this, marine models enable someone to have a preview of a ship before construction of a vessel through trial and error in order to reach the most proper design. They assist engineers and designers in the determinations of problem areas and solutions before drawing sets of final designs, thus delivering most efficient and effectual ships. Collectibles and Exhibitions: Some of them are built to such detail that they are close to life-size and are displayed in museums, exhibitions and as private collections. They are traditional, as well as contemporary; they are outstanding in terms of craftsmanship and are associated with historical events. Training and Simulation: Marine models are employed in the training instances to replicate the ship operations and the prevailing situations. All of the material has clearly practical application, showing how such vessels perform, and how they interact in different conditions, without actual sea and ocean tests and trials. Historical Preservation: This way, crucial details of historic vessels can be reproduced thus helping to keep that part of maritime history alive. These models are very useful in preservation of history, as far as the older designs and technologies are concerned. Define Marine Model Making Marine model making is really the art and science of re-creating mini-vessels with precision. It is a process that involves a number of technical skills combined with the artistic design of capturing the essence of the original vessel. Marine model making can be used in hobbies and some applied areas, such as education, design, and display. What makes marine modeling so critical is the ability to use small forms of representing complex ships and boats. Whether the models are for educational purposes, validation of the design, or just mere showpieces, they have to be properly planned for both their design and execution. The process of marine model making The process of marine model making is a process that describes how a model is made from the time an idea is conceived in the designer’s mind to the time the model is ready to be displayed. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you understand how these intricate models are created: Research and Planning Gather Information: The first step is understand all the specifications of the vessel that is to be modeled. They include drawings, previous records, and comparison pictures. Special emphasis shall be put on the data accuracy since a faithful representation cannot be obtained with inaccurate data. Define Objectives: Find out the goal or objective of your model. It will also help to guide the process of designing and building your Verismo, whether it is for educational use, design verification, or as a freak fixture, so to speak. Design and Prototyping Create Initial Designs: Develop rough outlines in sketches or computer generated graphic impressions for the model. It thereby enables one to have a feel of the final work and probably how the construction process will look like. Build Prototypes: Make models in the form of rough designs so that you can pilot the plan that you wish to execute. It gives an opportunity to modify something and guarantee that the designed item is practicable and correct. Materials Selection Choose Materials: Choose the right materials for your marine model based on your model’s purpose and desired level of detail. Key materials include fiber, acrylic, and 3D printing. Each material offers unique characteristics and finishes suited for different aspects of model making. Prepare Materials: These activities include cutting, shaping, and forming of the materials ready for assembly. It stresses that you must have all the parts that are required in constructing the house before you embark on the construction. Construction Assemble the Hull: Start off by building the structure of the vessel commonly known as the hull. This base part has to be perfectly measured and put together with precision. Add Details: After the construction of the hull, such elements as decks, superstructures, and fittings can be installed. When addressing these points, one should employ precision tools so as to achieve relative simplicity yet a high degree of accuracy and interconnectivity. Finish and Paint: Paint the model and add any finishing touches to make it resemble the real ship. This entails putting on trims, weathering, and other features that will make the model look more realistic. Final Assembly and Testing Assemble Components: Place all the elements together and make sure all the joins are right and tight. Test and Review: Check the entire accomplished model for its precision and high quality. This way, you can make any necessary adjustments that would make it fit your desired look and feel. How to Make a Marine Model If you want to know how to make a marine model you have come to the right