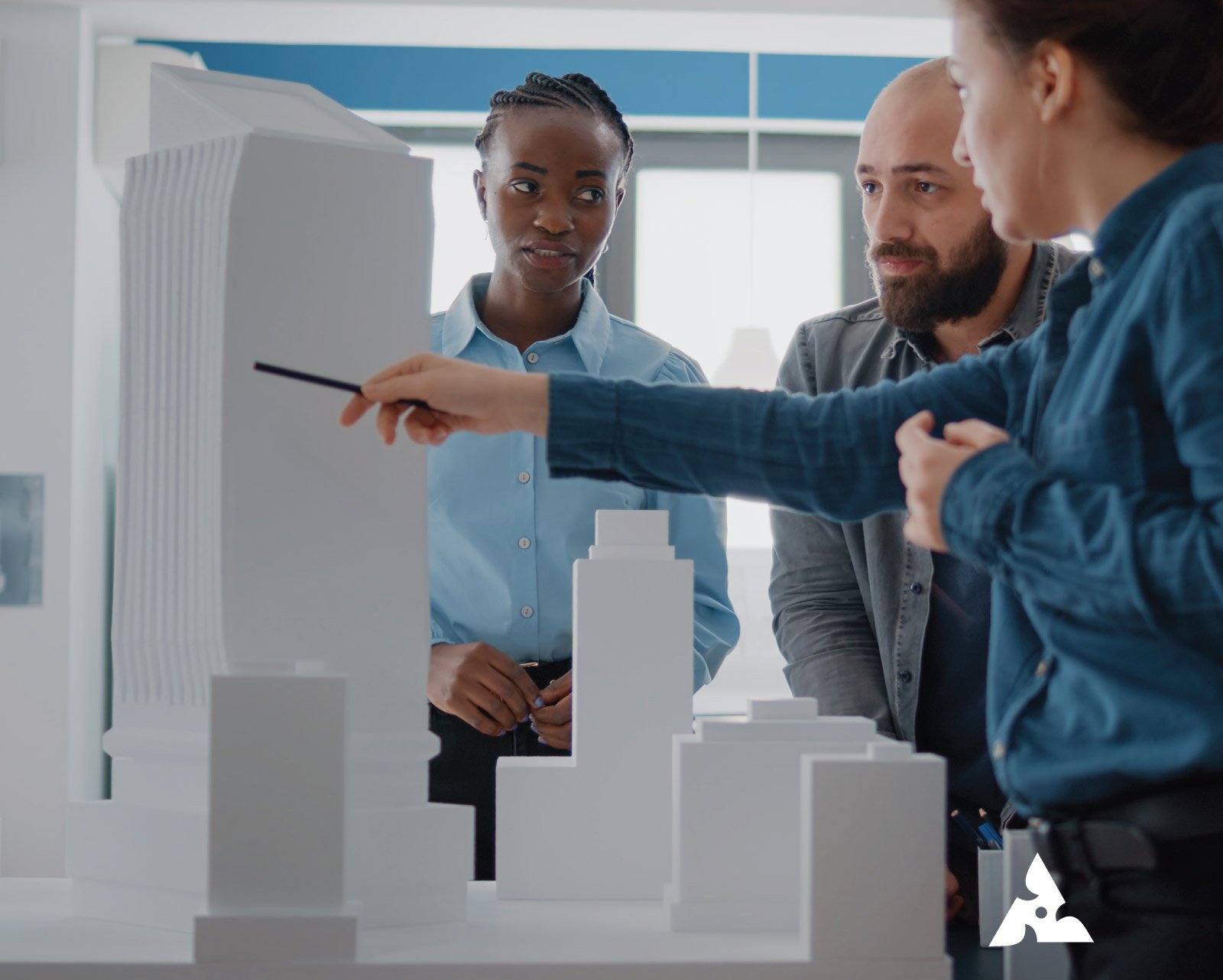
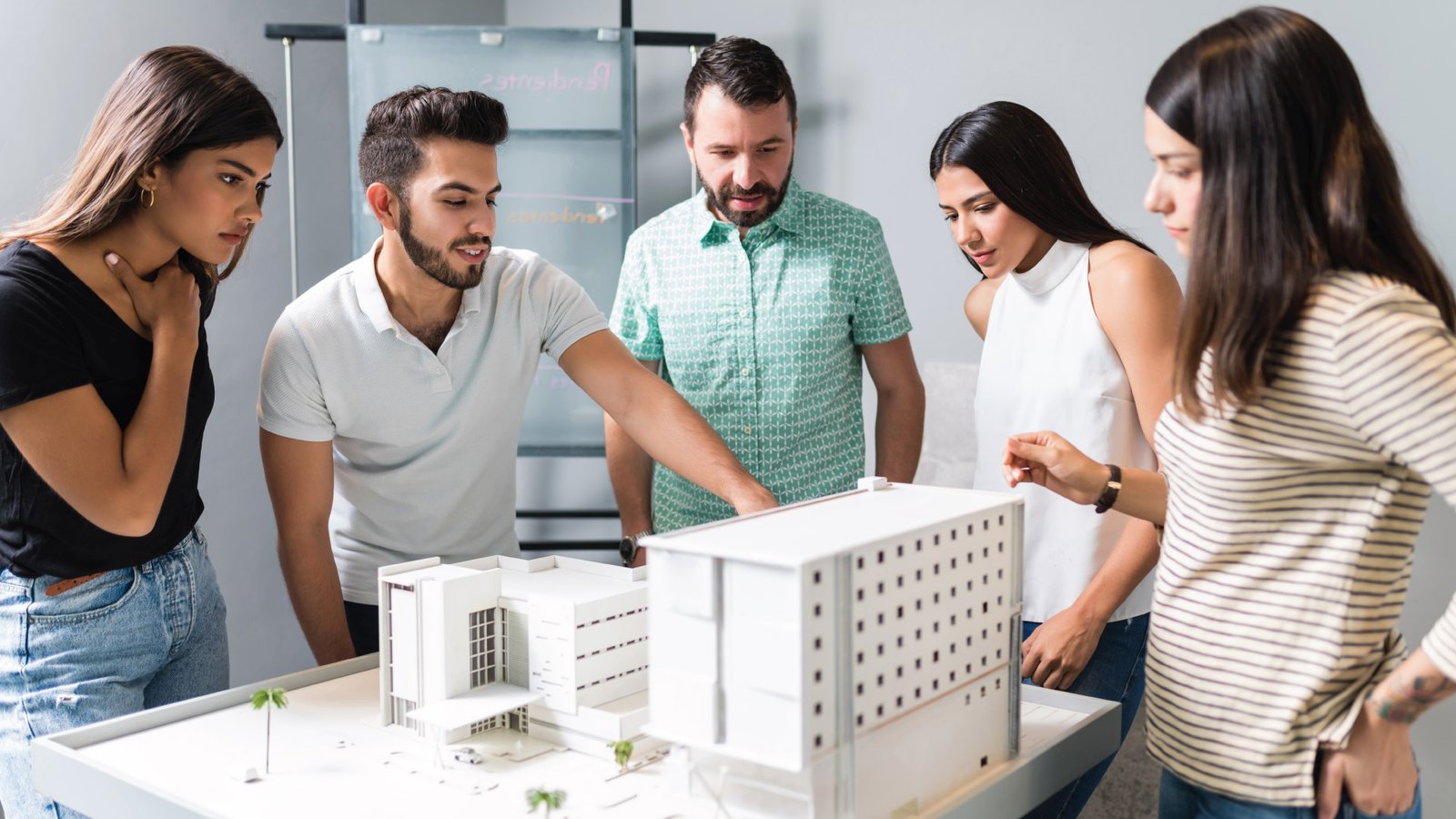
How 3D Printing is Revolutionizing Scale Model Making in 2025 Table of Contents Let’s Connect 3D printing has also revolutionized scale modeling, as with other sectors. From architect, engineer, and designer to hobbyist, and everything in between, 3D printing scale models have opened up new realms of creativity, accuracy, and efficacy. Complex, detailed models are now possible high-speed and at less cost. Prototyping takes but a jiffy; the most minute details on a miniature piece find their place through 3D printing. Here, in this blog post, we shall talk about the effects that 3D printing has on model making in the year 2025 and why it is an indispensable procedure in miniature models as well as other scale model production. The Role of 3D Printing in Modern Model Making For many years now, scale modeling has played a fundamental role in architecture and product design as well as entertainment. One aspect of using the antiquated practice of handcrafting every single element that constitutes a model is obviously both time-consuming and costly. However, with the new 3D printing for scale models, the whole process revolutionized into a faster, more precise, and much more efficient one. 3D printing enables designers to create a model directly from digital files, which eradicates the necessity for manual assembly or molds. The output of this is very accurate and realistic representation of a design, and it would be produced with minimal waste and in a fraction of the time it could take with traditional methods. 3D printing model making has now become a common technique for architecture up to video game design. Precision and Detail: The Power of 3D Printing for Scale Models First and foremost, it is through 3D printing of scale models that will possibly allow an extremely high level of detail and precision. In contrast to this scenario, in traditional model-making, inconsistencies and imperfections would have resulted from handcrafting based on the workers’s expertise. In the case of 3D printing, on the other hand, every detail, from the smallest details to complex geometries, is under control. For example, if architects design 3D-printed miniatures, they can really ensure that every little detail, from the windows to roof structures, is repeated with rather accurate precision. This would also be about the ability to produce very complex and intricate shapes in terms of texture that might prove impossible or hard to create by hand. For instance, in the film industry, highly detailed miniatures for video games and other media require 3D printing as an inevitable tool that cannot be done without. The designers can create miniature models of characters and other vehicles or even settings according to original designs with a touch of realism never before seen. Speed and Cost Efficiency: How 3D Printing Streamlines Model Making Another major benefit 3D printing provides model makers is the time to produce models. Traditional model-making may consume days, weeks, or even months, depending on the complexity of the job, whereas 3D-printed miniatures could be completed in a portion of this time. Models are produced layer by layer directly from a digital file, thus, 3D printing accelerates production by several folds. It means this speed is particularly useful in the industries, and it allows the designers and engineers to design lots of prototypes, check them out, adapt them, and iterate on their designs in a short period of time. For example, designers of new products can produce a gadget or device prototype, test its functionality, and modify it accordingly based on feedback within a few days. In addition, 3D printing is way less expensive than any traditional model-making. This digital process does not require very expensive molds, costly tools, or very expensive labor. Furthermore, since the material is applied only where necessary, waste is very limited, so this is the perfect process, both environment-friendly as well as budget-friendly. The Versatility of 3D Printing in Scale Model Making 3D printing scale models highly lend themselves to adaptability. Here, the process in model making primarily employs a specific group of materials, such as foam, wood, or plastic, which must be shaped along with the time necessary for the creation of each model, yet 3D printing can be done on a variety of materials, from plastics and resins through to metals and even flexible filaments. This flexibility is particularly useful in architectural and product design areas, where the choice of material may have a heavy impact on the final model’s texture, appearance, and durability. The designer can opt for the ideal material for the project, from a miniature game model made by 3D printing to a large-scale architectural model. Moreover, 3D printing also makes accessible structures and geometries in many places that would be impossible or very challenging to attain otherwise. For instance, a curved wall or a particular part would be much easier to achieve using 3D printing. Such possibilities open huge scopes for creativity and innovation in designs as well as new ways of working with scale models in different types of industries. Case Studies: Real-Life Applications of 3D Printing in Scale Model Making Scale Model Making Applications of 3D printing in scale models range from a variety of sectors and stand at incredible numbers. Here are a few examples of real-life applications: Architecture: Many architecture firms today use 3D printing scale models to actually visualize the designs before construction on-site starts. The minuscule models are highly detailed and provide architects themselves and even their clients with excellent views of the scale, proportions, and aesthetic qualities of the designs. In fact, some firms also make use of 3D printing for intricate urban models that show where the new buildings will fit in with the existing landscape of the city. Product Design: A product designer may prototype and test a new product using a 3D-printed miniature. An example is that a designer developing an entirely new electronic appliance can quickly come up with a 3D-printed prototype to check the form and fit functionalities. The product would then be developed at