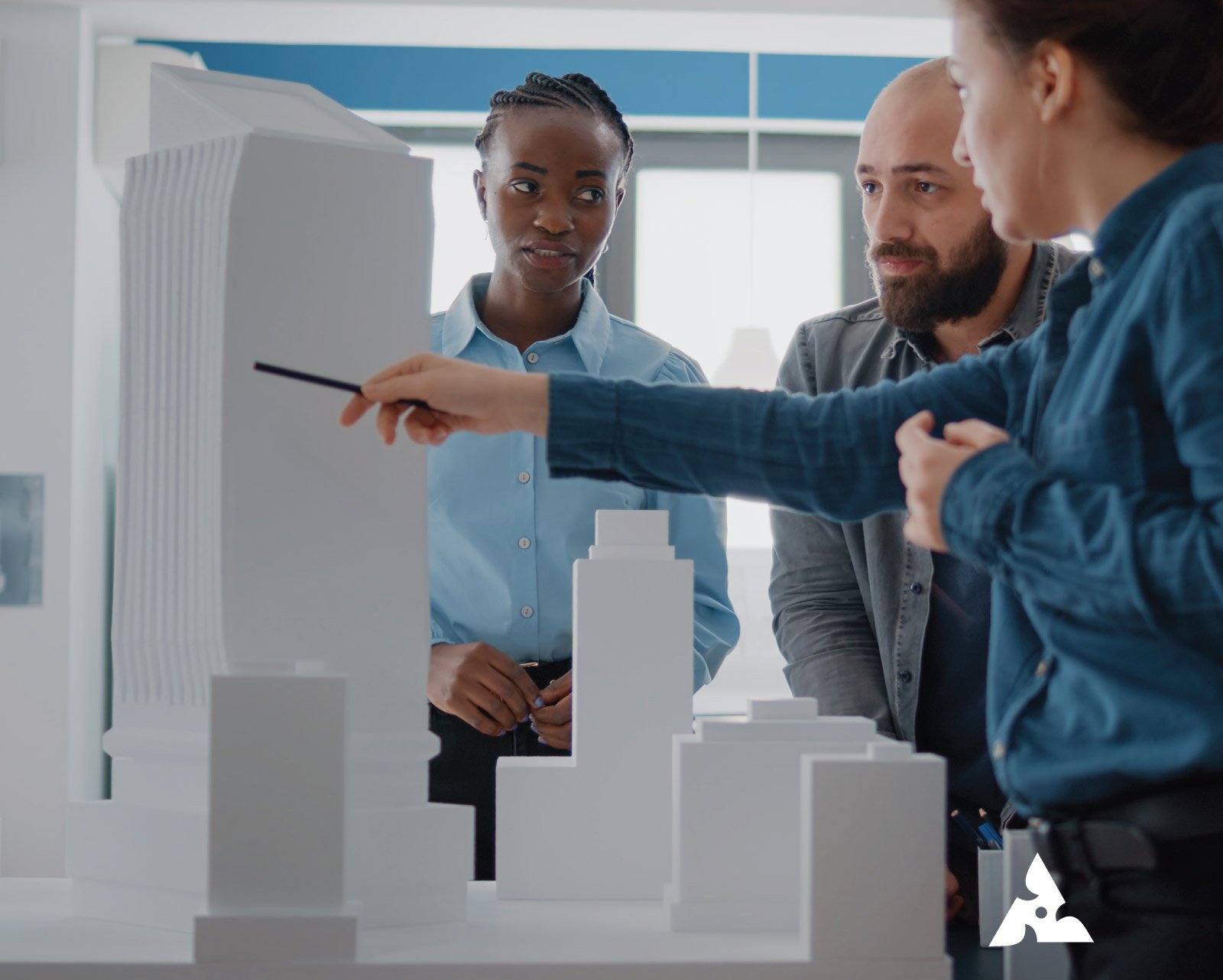
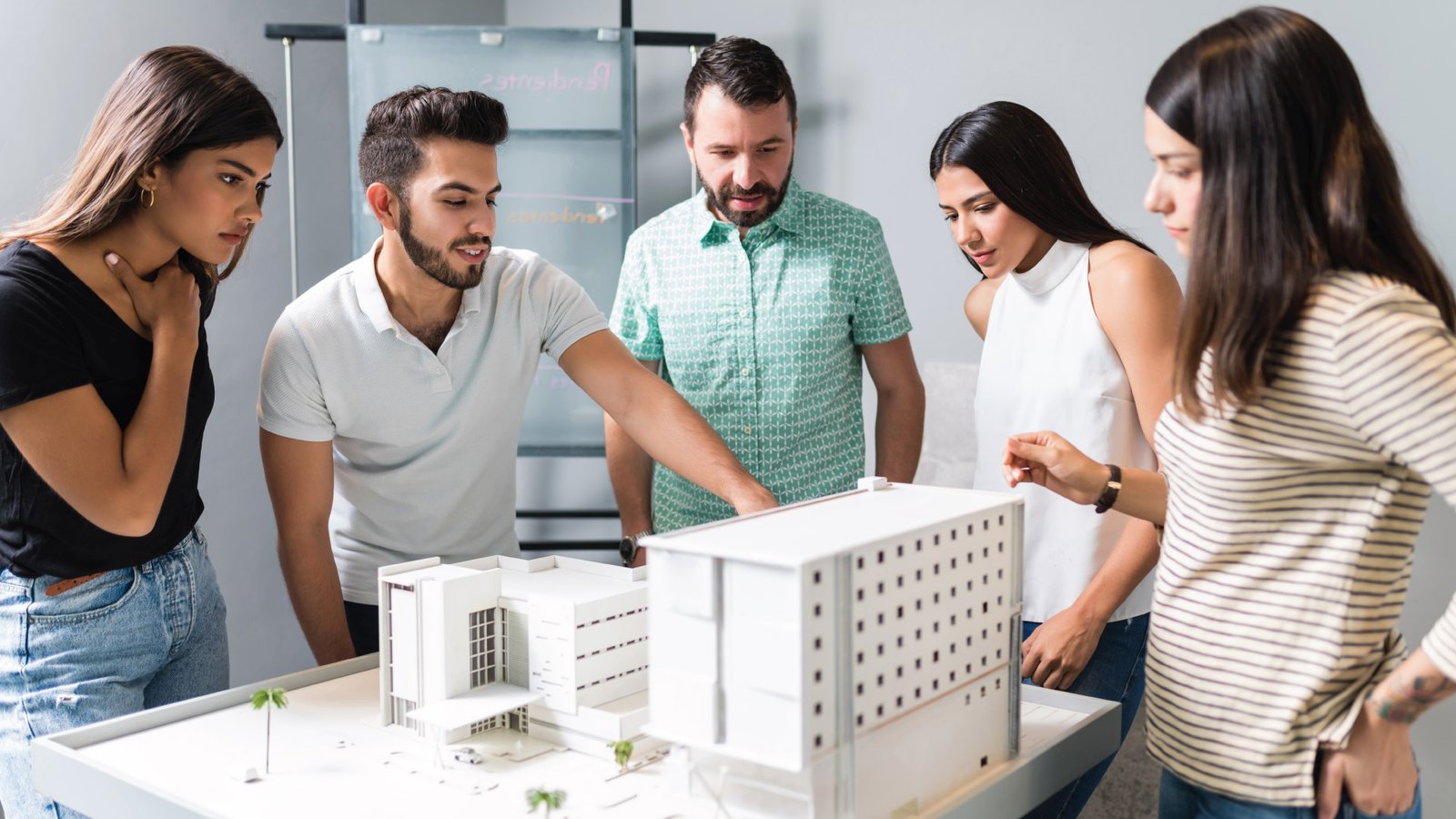
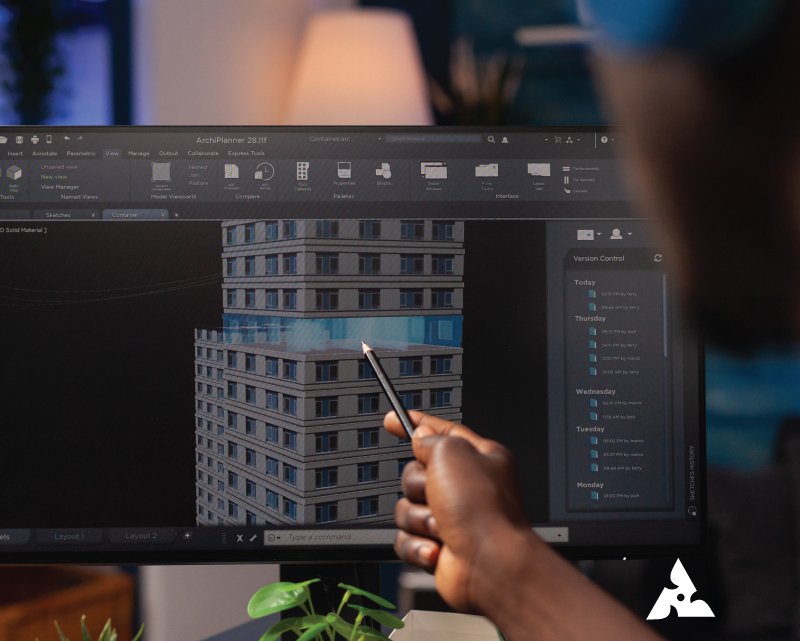
What is 3D Rendering? How to Create High-Quality 3D Models for Beginners Table of Contents Get A Free Quote 3D rendering describes the generation of an image from a 3D model made in specialized computer software. The outcome, whether a realistic or stylized view, is representative of an object, scene, or environment. Such techniques are of great importance in diverse industries such as architectural visualization, product design, and gaming. As demand for very appealing visual content increases, the ability to produce great 3D models becomes an imperative for any aspiring artist. In this blog post, we shall explore the standards of 3D rendering, give you a few tips on producing excellent 3D models, and describe how 3D rendering finds application in several industries.Be it from a hobby perspective, a consideration for an aspiring artist, or an interest in working with the business side of 3D rendering, the information provided on this basis should give you a head start. What is 3D Rendering? 3D Rendering is the process of creating 2D images and animations from a 3D model with the help of the software. It is equivalent to a photograph but instead captures a model made with the computer. This helps to simulate, using texture, lighting, and camera settings in the rendering of images, a real-world condition in which the final image looks as realistic or stylized as desired. Basic Steps to Doing 3D Rendering: Modeling: To create a 3D object or environment representation. Texturing: Add surface details like color, patterns, and materials to the model. Lighting: Position virtual light sources to obtain the required effects of brightness and shadow. Rendering: The final step where a computer generates a two-dimensional image from a three-dimensional model. History of 3D Rendering 3D rendering basically started during the advent of some initial computer graphics around 1960 with early works like Ivan Sutherland’s Sketchpad. More advanced ones appeared from about 1970 through the 1980s, with the very first of the CGI films, Tron (1982), claiming example early work in 3D rendering. By the mid-1990s, neo-sophisticated modeling software such as Autodesk’s 3ds Max and Maya became industry standards. The advancement of the new millennium saw advances in real-time rendering, boosted by gaming and VR, pushing for realistic modeling of 3D figures. From ray tracing to artificial intelligence technology, rendering in three dimensions keeps changing even today. How to Create High-Quality 3D Models for Beginners For a beginner, creating high-quality 3D models might sound a weighty challenge when one imagines it. But with the right instruments, the correct processes, and with some practice, anyone can start producing quite impressive 3D visuals. So, here is a simple stepwise approach to take a beginner through some steps of learning howHere is a simple step-by-step procedure for a novice to the task to learn how to create 3D models such as: to make 3D models. 1. Learn the Basics of 3D Modeling In order to create good-quality 3D models, one must learn the very basics of 3D modeling. Different types of modeling techniques exist, including polygonal modeling, NURBS modeling, and sculpting. For beginners, polygonal modeling is a great starting point because it creates a 3D object by connecting vertices, edges, and faces. 2. Choose the Right 3D Software There are many software programs available for 3D modeling and rendering. Some of the most popular ones include: Blender: A free and open-source 3D modeling and rendering software that’s ideal for beginners. Autodesk Maya: A professional-grade software often used for animations and character modeling. Cinema 4D: Known for its intuitive user interface, Cinema 4D is great for beginners and intermediate users alike. SketchUp: A user-friendly software that is widely used in architectural visualization. Selecting the right software depends on your personal preferences, the complexity of your projects, and your budget. 3. Focus on Accuracy and Detail Creating a high-quality 3D model requires attention to detail. Pay close attention to proportions, measurements, and scale to ensure that your models are realistic. Add intricate details such as textures, materials, and realistic surface imperfections (like scratches, dirt, and rust) to make the model feel lifelike. 4. Master Texturing and Shading Textures bring your 3D models to life by giving them realistic surface qualities. Learn how to apply textures, such as wood grain, fabric patterns, or metal finishes, to your models. Shading is also crucial in achieving the right look for your model, as it controls how light interacts with the surface. Invest time in understanding these elements to enhance the visual appeal of your 3D models. 5. Experiment with Lighting Lighting is an essential aspect of 3D rendering that greatly affects the final output. It’s important to experiment with different light setups and placements to find the most flattering arrangement for your model. Use light sources such as spotlights, area lights, and ambient lights to create depth, mood, and realism in your renders. 6. Rendering and Post-Processing Once your model is ready, it’s time to render it into a final image or animation. Most 3D software comes with built-in rendering engines, but you can also use third-party renderers like V-Ray or Arnold for more advanced features. After rendering, use post-processing software like Photoshop or After Effects to enhance the final image by adjusting colors, adding effects, or improving contrast. The Role of 3D Rendering in Business and Industry The use of 3D rendering has expanded far beyond just entertainment or design purposes. It has found its way into various industries, including architecture, real estate, and product design. Let’s take a look at some key industries that benefit from 3D rendering. 1. Architectural Visualization and Rendering Architectural 3D rendering is one of the most popular uses of 3D rendering technology. It allows architects and designers to create photorealistic images of buildings, interiors, and landscapes before any physical construction begins. This helps clients, stakeholders, and investors visualize the final product, make informed decisions, and catch potential design issues early in the process. For instance, a 3D architectural visualization and rendering company can provide realistic visual representations