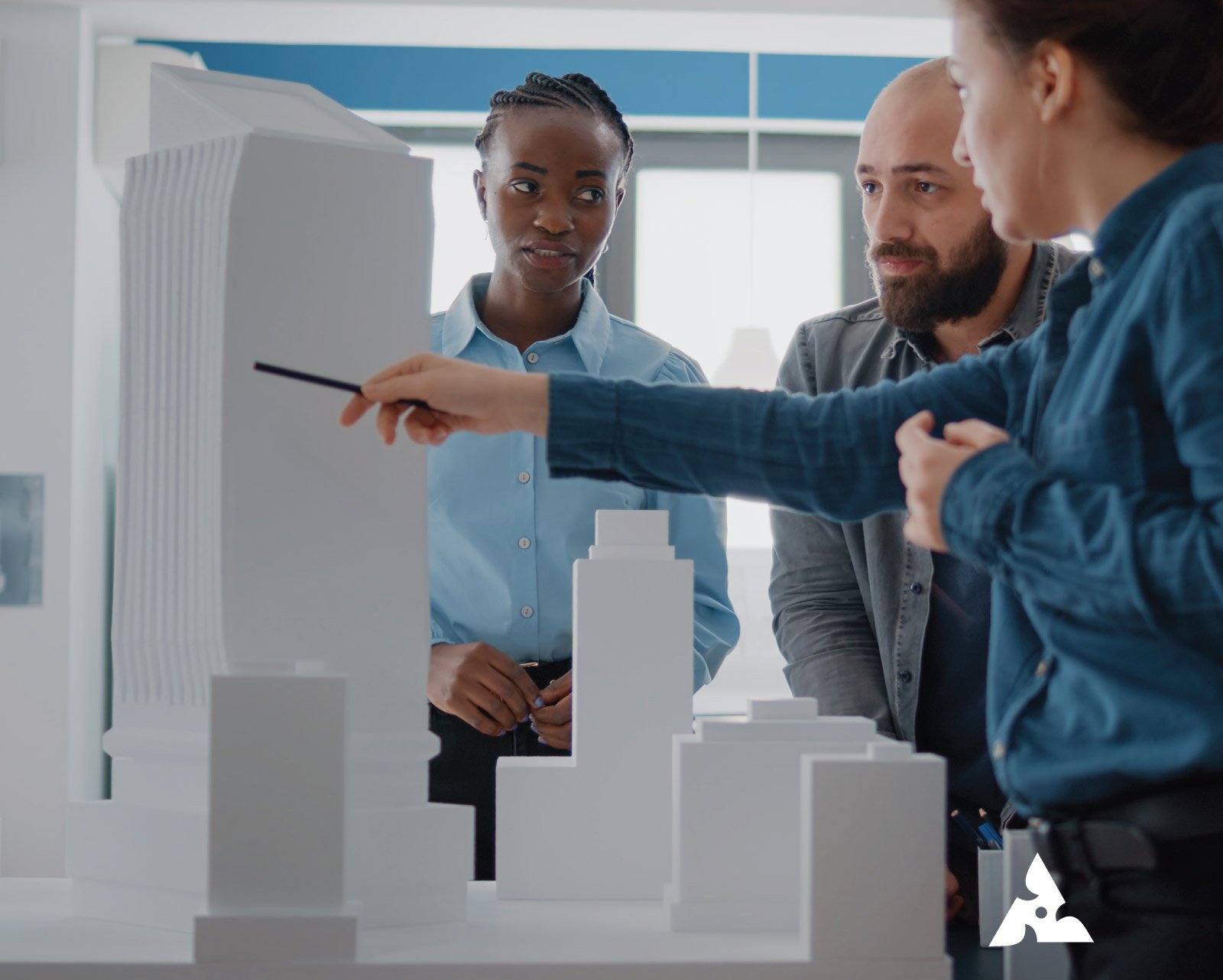
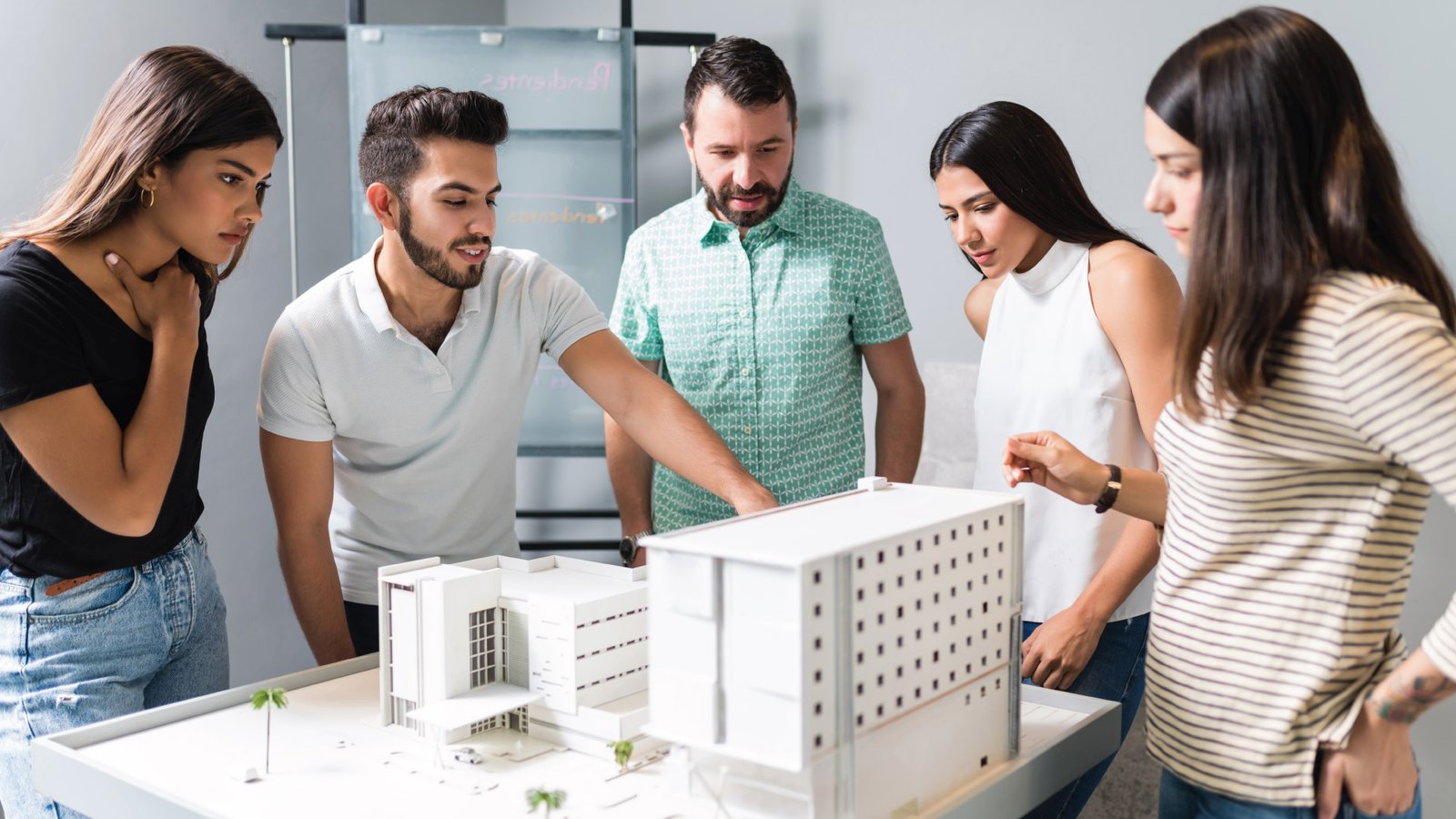
Discover the power of prototyping models to transform creative ideas into precise and realistic scale models. From the innovations of Leonardo da Vinci to the architectural vision of Frank Lloyd Wright and the engineering brilliance of Gustave Eiffel, prototypes have played a vital role in design success. This guide explains how rapid prototyping, mockups, and detailed models can improve accuracy, reduce errors, and help you create impressive miniature projects with confidence.