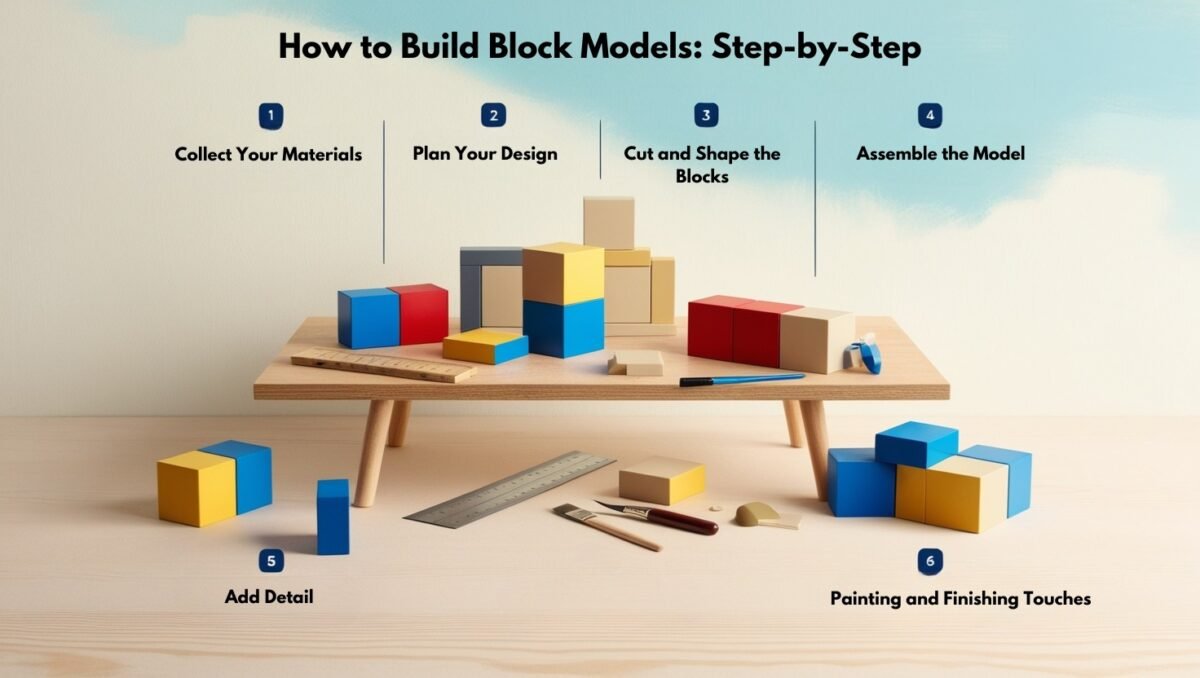
Exploring Architectural Block Model Making: Tips and Tricks Table of Contents Get A Free Quote Block model-making is an important skill in architecture because it helps designers and architects visualize their ideas in a three-dimensional form. For a first-time designer or an experienced designer, the block model kits can act as a source of hands-on tools that help sketch the architectural concepts envisioned by a person. In this blog, we will discuss tips and tricks on block model making, the best block model kits, and how to create detailed, custom block models for professional projects and hobbyist designs. Understanding Block Model Kits The block model kits would be a great starting point for beginners in architectural modeling. The kits come with everything you need to get started, such as wooden or foam blocks, cutting tools, and at times, even paints. The instructions or guides accompanying them help you build your first model on the block model kits for beginners. Choose a kit that best suits your design needs. There are kits that provide blocks of various sizes and shapes while others are dedicated strictly to detailed architectural models. Whether you’re doing simple layouts or more complex models, the right kit is what makes it. What is Block Model Making? Block model making is the creation of an architect’s three-dimensional model of a building or any structure designed using blocks, which can be made from wood, foam, or plastic. These are models created, that the architect can take to others to present their ideas visually. Model buildings can differ in complexity from simple structures to details in architects’ architectural plans. This technique helps architects and designers see their ideas from different angles and helps in communicating the vision of a project to clients, builders, or the public. Block model architecture is all about translating complex ideas into simple, understandable forms. How to Build Block Models: Step-by-Step If you’re wondering how to build block models, here’s a simple guide to help you get started: Collect Your MaterialsGet the basic materials that would be used. First off, you could purchase block model kits or even separate blocks according to your desire. You’ll then need your cutting tools, some glue, and paint for completing. Plan Your DesignBefore you start building, plan out a design for your model. Use the architectural drawings or sketch a new concept to keep in mind and guide you. This will let you know which blocks to put where and how to use shapes. Cut and Shape the BlocksUsing the blocks in your kit, now begin to cut and shape to match up with your building design. This could involve trimming, sanding, or simply stacking to create your building structure. Precision is paramount here, but don’t worry if you’re a beginner, “practice makes perfect”! Assemble the ModelNow that your blocks are shaped and ready, start to assemble them one by one. Place a small amount of glue for each block and make sure that they are held in place.Be patient with the model; make sure that it is stable and the design is as accurate as possible. Add DetailThis is what differentiates a block model from basic models; details such as windows, doors, and other architectural features. For more minute details on your structure, you may use smaller blocks or carving tools. It’s time to get creative at this stage. Painting and Finishing Touches After you’ve built your model, it is time to make it look even more real with paint. Painting block models can help to make them appear much more realistic. It would be ideal if you use the actual paint colors from real-world materials you are mimicking. To give it even a more real touch, add textures like wood grain or brick patterns. Custom Block Models: Taking Your Designs Further Custom block models are a perfect option for the more experienced model maker, as they allow you to personalize your designs. While standard kits are ideal for beginners, creating custom models will allow you to create something truly unique. Maybe cut your blocks to specifications, mix different materials together, or bring in details that these kits would have overlooked. Working on custom block models is a time to experiment with different textures and finishes. The personal touch to your block model architecture will not only make it stand out but also help in refining your skills as a model maker. Block Model Scenery: Adding Context to Your Designs Beyond the building itself, the addition of block model scenery to your building can add to creating a full and lifelike model. Scenery includes trees, roads, and land features that all add context to the building in its environment. Block model scenery can also be fabricated using small blocks or grass clumps to provide with miniature buildings, figures, and even textured paints for ground surface simulation. All this detailed work helps the viewer understand where your design fits within its surroundings, making it that much more impactful. Tips for Painting Block Models Painting your block models is possibly one of the most enjoyable parts of block model making. Painting your block models brings color, depth, and texture. Here are some dos and don’ts so you can paint your models effectively: Use Acrylic Paints: Acrylic paints are best for model making because they dry fast and can be applied easily on most block materials. Thin Your Paints: For your smoothest finishes, thin your paint slightly with water before painting. This helps avoid streaks and brush marks. Layering for Depth: Be not afraid of layering your paints. Apply a base coat, then a series of additional lighter or darker shades to create depth and dimension. Use Fine Brushes for Detail: A fine-tipped brush is perfect for adding on intricate details like window frames or texture lines. Conclusion It’s rewarding and very creative to build block models whether for professional architectural projects or to make detailed models for the hobby. Through the use of block model kits, learning how to build