Architectural Models: Definition, Types, Objectives, and Purpose
Table of Contents
Introduction
Architectural models are indispensable tools in the design world, helping transform abstract ideas into clear, visual representations. These models allow architects, clients, and stakeholders to see and understand what a building or structure will look like before it’s constructed. In this blog, we’ll break down what architectural models are, explore different types, discuss their objectives, and straightforwardly understand their purposes.
What Are Architectural Models?
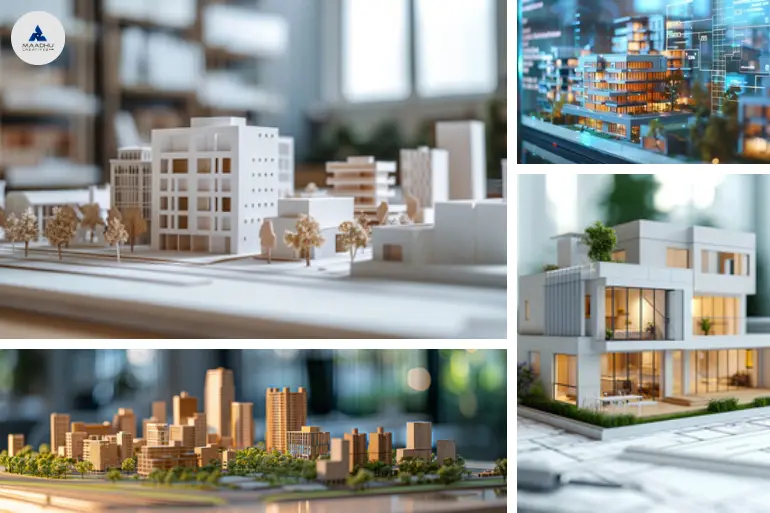
Architectural model definition : Architectural models are scaled-down representations of buildings or structures. They can be physical models you can touch, digital models viewed on a screen, or a combination of both. These models are crucial in the design process because they help everyone involved visualize how a building will look and function before construction begins.
Model architecture involves creating these detailed representations to ensure that every aspect of the design is clear and well thought out. Whether it’s a small physical model or a detailed digital one, these models make the design process smoother and more efficient.
Types of Architectural Models
Architectural models come in various forms, each serving unique purposes:

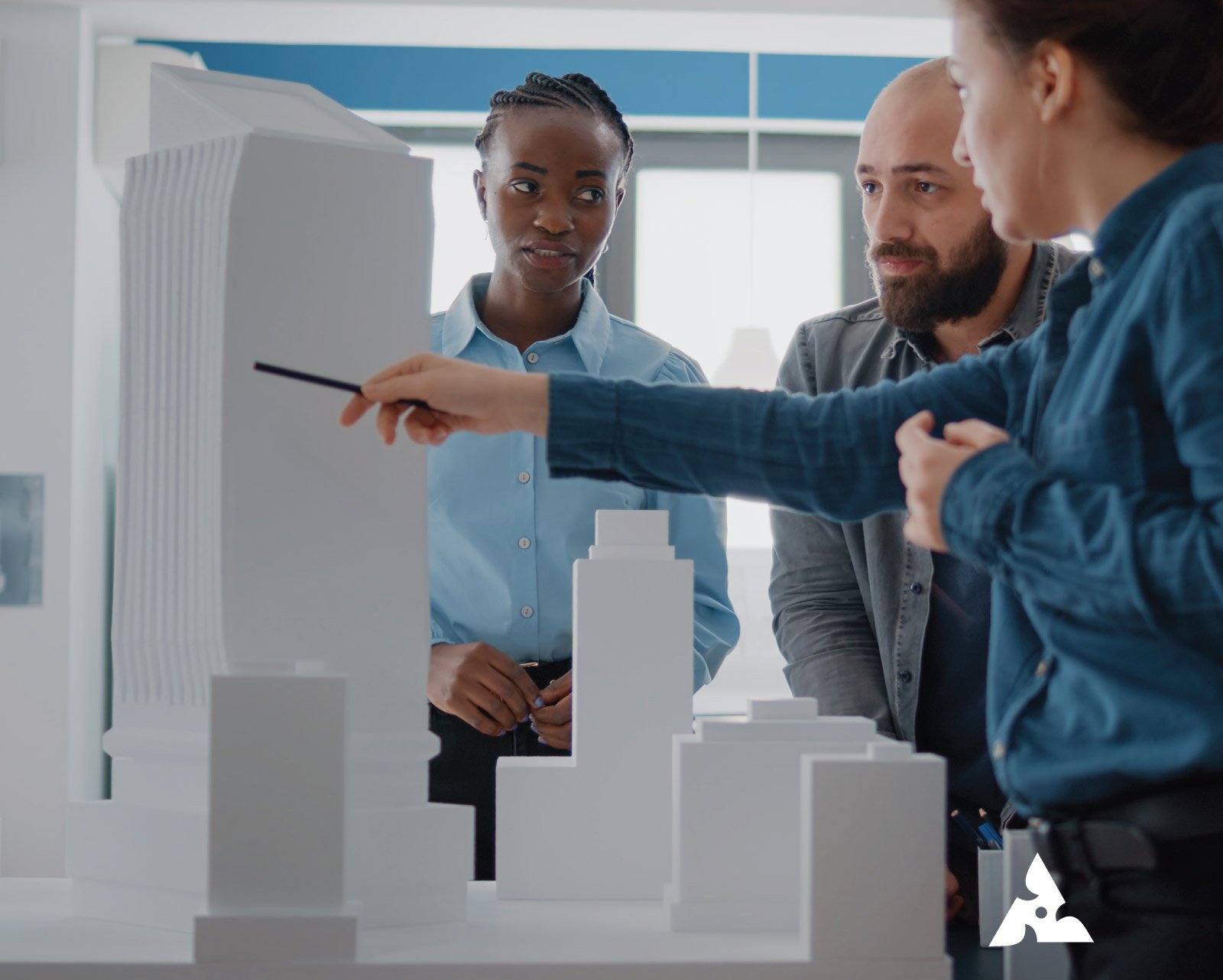
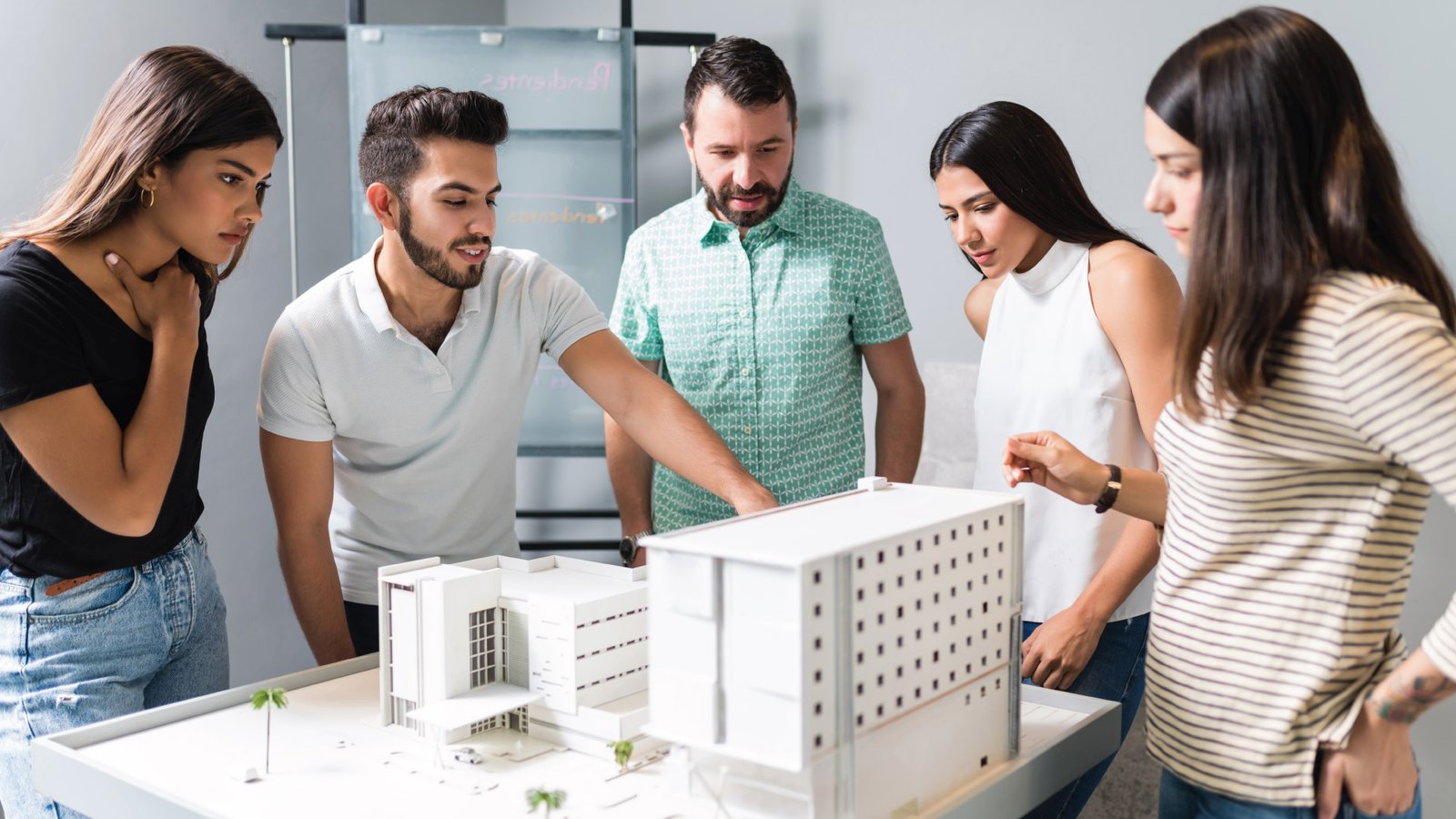
- Physical Models definition: These are three-dimensional, tangible models made from materials like cardboard, wood, or plastic. Physical architectural models offer a hands-on experience, allowing you to see and touch the design. They are often used in presentations to help clients and stakeholders visualize the final product.
- Digital Models: Created using computer software, digital models provide a virtual view of the building. You can rotate, zoom in, and view them from different angles. Digital models are excellent for detailed visualizations and simulations, letting you adjust and perfect the design before construction starts.
- Scale Models: Scale models are smaller, proportional replicas of buildings or structures, designed to represent the original in a reduced size while maintaining accurate proportions. For example, if a building is 100 feet tall, a scale model of that building might be 10 feet tall, keeping the same proportions and design features. These models are especially useful for making complex designs easier to understand and for presenting ideas. By providing a tangible and manageable version of the final project, scale models help architects, clients, and stakeholders visualize and evaluate the design before construction begins.
- Conceptual Models: These are simplified versions used for brainstorming and exploring ideas. They are not as detailed as physical or digital models but are useful in the early stages of design to quickly test different concepts.
Objectives of Models For Architecture
Architectural models serve several important functions in the design and construction process:
- Visualization: One of the main goals of architecture modeling is to provide a clear view of what the finished building will look like. This helps architects and clients see how different parts of the design come together and make necessary changes before construction begins.
- Communication: Models are powerful tools for communicating design ideas. They make complex concepts easier to understand and discuss. Architects use models to explain their visions to clients, builders, and other stakeholders, ensuring everyone is on the same page.
- Decision-Making: By examining a model, architects and clients can make informed decisions about materials, colors, and layouts. This helps avoid costly changes later on and ensures the final design meets everyone’s expectations.
- Testing and Analysis: Models allow for testing various design aspects, such as how natural light will affect the building’s interior or how the structure fits into its surroundings. This helps identify potential issues and refine the design before construction begins.
The Purpose of Architectural Models
The purpose of architectural models is multi-faceted and essential for successful design:
- Enhance Understanding: Architectural models provide a clear and tangible way to grasp how a building will look and function. They help visualize the design in 3D, making it easier to understand how different parts come together.
- Improve Design Quality: By allowing designers to experiment with various ideas and see them in action, models help enhance the quality of the final design. This results in better outcomes and fewer changes during construction.
- Facilitate Collaboration: Models serve as a common reference point for everyone involved in the project. This helps architects, clients, and builders discuss and agree on design details more effectively.
- Engage Stakeholders: For larger projects, models are useful for engaging the public and other stakeholders. They provide a clear representation of the project, helping gain support and gather feedback.
Types of Models in Architecture
In model architecture, different types of models are used at various stages of design:
- Architectural Exterior Models: These focus on the outside appearance of the building, including the facade, materials, and how the building fits into its environment. They help visualize the final look and feel of the structure.
- Architectural Interior Models: These focus on the interior layout, including spaces, furniture, and lighting. They help in designing functional and visually pleasing interior environments.
The Role of 3D Modeling in Architecture
Architecture modeling has advanced significantly with the introduction of 3D technology. Digital 3D models offer detailed visualizations and simulations that traditional 2D drawings cannot provide. This technology enables architects to explore designs more deeply, make real-time adjustments, and present their ideas more effectively.
With 3D modeling, architects can create highly detailed and accurate representations of their designs. This allows for better exploration of design options, more precise adjustments, and clearer communication of ideas.
Conclusion
Architectural models are crucial for bringing building designs to life. They help us see and understand how a structure will look and work before it’s built. By using different types of models, such as physical, digital, or scale models, architects and designers can better communicate their ideas and make sure everything is just right. These models make it easier to spot potential problems and refine the design to meet everyone’s expectations. Whether you’re an architect, a client, or just someone interested in design, understanding and using these models can make the entire process smoother and more successful.
FAQ's
An architectural model is a smaller, simplified version of a building or structure. It’s designed to help people visualize and understand how the final project will look, even though it’s much smaller than the actual structure. It can be a physical model you can touch or a digital model you view on a screen. These models help visualize how a building will look and function before it’s built.
The main types of architectural models are physical models, digital models, scale models, and conceptual models. Each type serves different purposes, from hands-on visualizations to detailed virtual simulations.
A scale model is a smaller, proportional version of a building or structure. For example, if a building is 100 feet tall, a scale model might be 10 feet tall, maintaining the same proportions. This makes it easier to understand the design in a manageable size.
3D modeling allows architects to create detailed and accurate representations of their designs. It provides a more in-depth exploration of design options, enables real-time adjustments, and enhances communication through detailed visualizations and simulations.
Architectural models help visualize the final design, communicate ideas more clearly, make informed decisions, and test various aspects of the design. They enhance understanding, improve design quality, facilitate collaboration, and engage stakeholders.