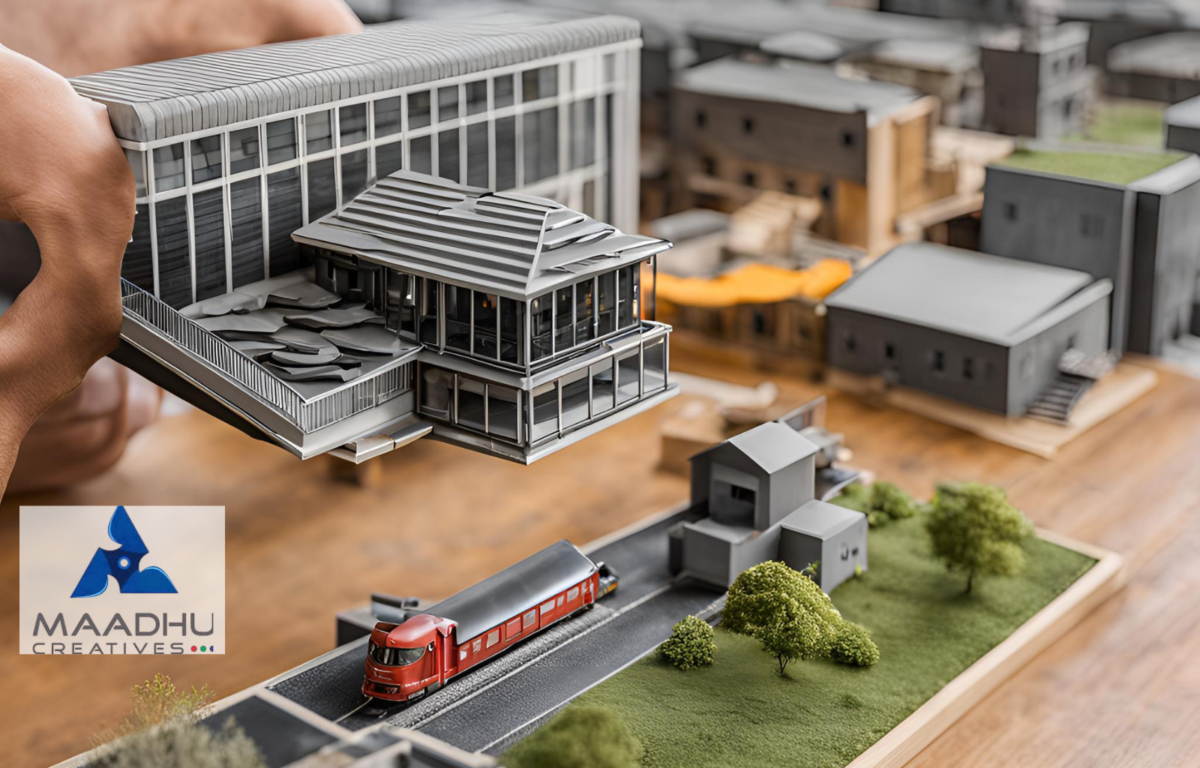
What is and type of Scale Model and How Do You Create One?
Table of Contents
Introduction
A scale model is a smaller, physical version of something real, keeping all the important details in proportion. “Scale” means the model’s size compared to the real thing. People use scale models in fields like architecture, engineering, film, and hobbies to see and understand how something looks and works.
Importance of Scale Models
Scale models play an important role in the design and development process. They help in:
- Visualization: Providing a tangible form of a concept that can be inspected from all angles.
- Testing and Analysis: Allowing for evaluating design elements and functionality in a controlled environment.
- Communication: Facilitating clearer communication of ideas between designers, clients, and stakeholders.
- Presentation and Marketing: Enhancing the presentation of ideas and designs to potential clients or investors.
- Education and Training: Effective tools for teaching and training in various fields.
Types of Scale Models
There are different types of scale models, each serving different purposes:
Architectural Interior Models
Architectural interior models provide a detailed, three-dimensional representation of a building’s interior design. These models showcase the layout, furniture, fixtures, and decor, allowing clients and designers to visualize and refine interior spaces before construction begins, ensuring optimal functionality and aesthetic appeal.


Architectural Exterior Models
Architectural exterior models illustrate the outer structure and facade of buildings. These models highlight the design, materials, and architectural features, offering a clear visual representation of the building’s exterior. They are essential for evaluating aesthetic appeal, contextual fit, and design coherence in the surrounding environment.
Engineering Models
Engineering models are precise mechanical, civil, or structural engineering project replicas. They demonstrate the functionality, design, and mechanics of complex systems, enabling engineers to test, analyze, and refine their designs. These models are crucial for identifying potential issues and optimizing performance before full-scale production.


Marine Models
Marine models are detailed representations of ships, boats, and other maritime vessels. These scale models are used for design evaluation, historical preservation, and educational purposes. They provide a comprehensive view of the vessel’s structure, layout, and design features, ensuring accuracy and attention to detail.
Piping Models
Piping models are scaled-down versions of piping systems used in industrial, commercial, and residential projects. These models illustrate the layout, connections, and flow of pipes within a system, aiding in design optimization, troubleshooting, and maintenance planning. They ensure accurate implementation and efficient system operation.


Master Plan Models
Master plan models depict large-scale developments, such as urban planning projects, campuses, or industrial complexes. These models provide an overview of the entire development, illustrating the spatial relationships, infrastructure, and landscape. They are essential for comprehensive planning, stakeholder presentations, and public consultations.
Industrial Models
Industrial models are scale representations of industrial plants, factories, and equipment. These models showcase the layout, machinery, and operational processes, allowing for detailed analysis and optimization. They are used for planning, training, and marketing, ensuring efficient and safe industrial operations.

The Scale Ratio

The scale ratio is a critical aspect of model-making. Common scales include:
– 1:10: Often used for larger models, such as industrial equipment or large buildings.
– 1:25: Commonly used for architectural models.
– 1:50: Suitable for detailed building models.
– 1:100: Used for site plans and smaller architectural details.
– 1:500: Ideal for city planning and large-scale landscapes.
Creating a Scale Model: Step-by-Step Process
Creating a scale model involves several steps, each requiring attention to detail and precision. Here’s a comprehensive guide to creating a scale model:
Planning and Research
Understanding the Project: Begin by gathering all necessary information about the object you are modeling. This includes dimensions, materials, design details, and functionality.
Choosing the Scale: Decide on the appropriate scale for your model. Consider the purpose of the model, the level of detail required, and the available space for display.
Sketching and Blueprinting:: Create detailed sketches and blueprints of the model. These will serve as guides during the construction process.

Gathering Materials and Tools
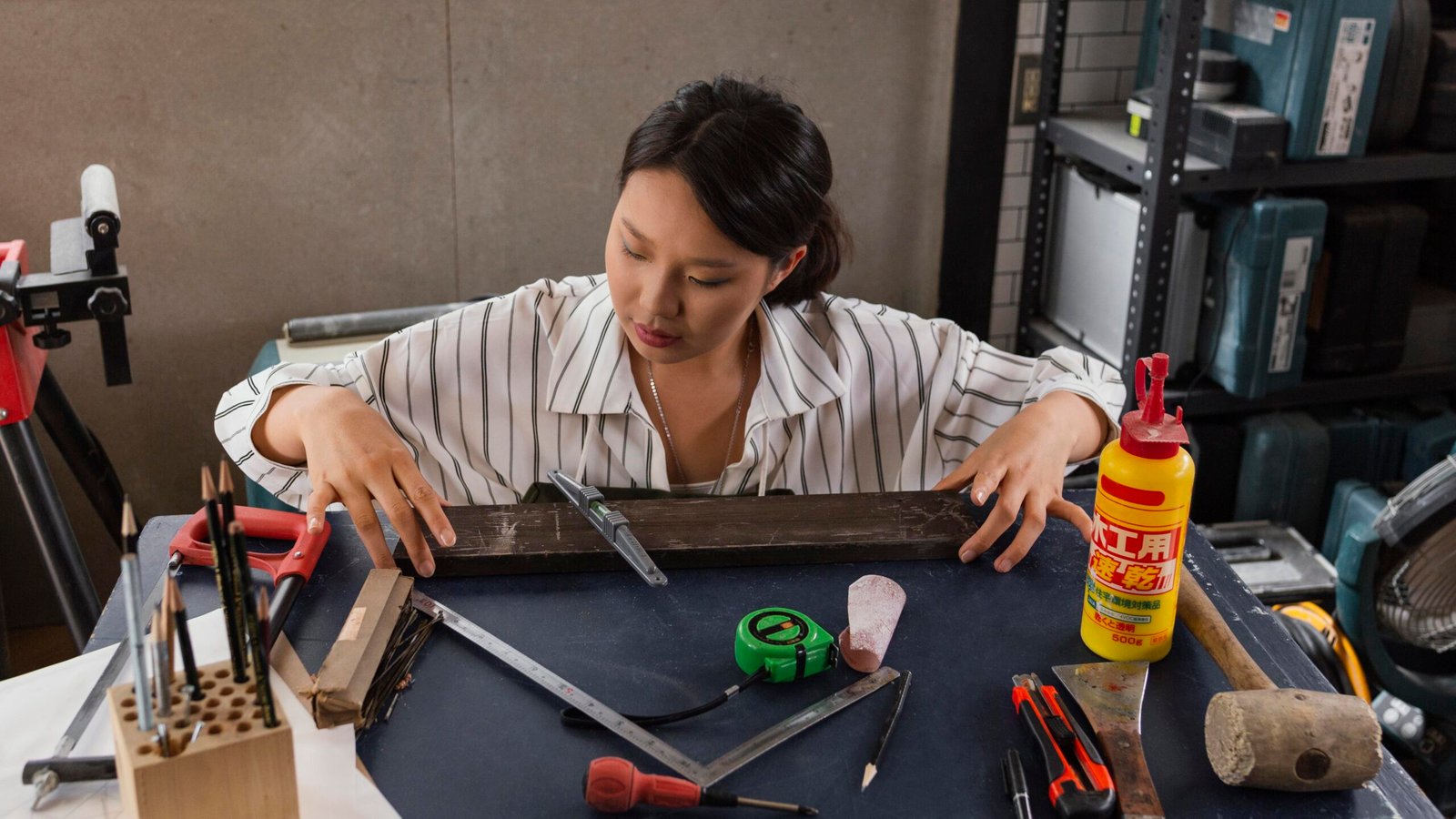

model making materials:
– Foam Board: Lightweight and easy to cut, suitable for basic structures.
– Plastic: Durable and versatile, used for detailed components.
– Wood: Provides a natural look and can be used for structural elements.
– Metal: Adds strength and realism, often used for intricate details.
– Paper and Cardboard: Ideal for quick prototypes and simple models.

Model making tools:
Essential tools for model-making include:
– Cutting Tools: X-Acto knives, scissors, and saws.
– Adhesives: Glue, tape, and epoxy.
– Measuring Tools: Rulers, calipers, and compasses.
– Shaping Tools: Sandpaper, files, and sculpting tools.
– Painting and Finishing Tools: Brushes, airbrushes, and paint.
Building the Base Structure
Cutting and Assembling: Start by cutting the base pieces according to your blueprints. Assemble the base structure using appropriate adhesives.
Ensuring Accuracy: Double-check measurements and alignments to ensure the model accurately represents the original design.
Adding Details
Layering: Add layers of materials to build up the model’s structure and details. Use thin layers for intricate parts to maintain precision.
Texturing and Shaping: Use tools to add textures and shapes that replicate the real object’s surface.
Detailing: Include small details such as windows, doors, and fixtures. These elements enhance the realism of the model.
Painting and Finishing
Priming: Apply a primer to prepare the surface for painting. This ensures better paint adhesion and a smoother finish.
Painting: Use appropriate paints to replicate the colors of the original object. An airbrush can provide a smooth, even coat, while brushes are suitable for fine details.
Weathering and Effects: Add weathering effects to enhance realism. Techniques like dry brushing, washes, and chipping can simulate wear and tear.
Sealing: Apply a clear coat to protect the paint and finish. This also gives the model a polished look.
Assembly and Final Touches
Combining Parts: Assemble the detailed components to form the final model. Use adhesives that provide strong bonds without damaging the details.
Inspection and Corrections: Inspect the model for any imperfections or inaccuracies. Make necessary corrections to ensure the model meets the desired standards.
Final Presentation: Prepare the model for presentation or display. This may include mounting it on a base, adding display labels, or placing it in a protective case.
Tips for Successful Scale Modeling
Patience and Precision: Take your time with each step. Precision is key to creating a high-quality model.
– Referencing: Continuously refer to your blueprints and reference materials to maintain accuracy.
– Experimentation: Don’t be afraid to experiment with different techniques and materials to achieve the desired effect.
– Practice: The more you practice, the better you’ll become. Start with simpler models and gradually take on more complex projects.
– Community: Join modeling communities or forums to share your work, gain feedback, and learn from others.
Conclusion
The process of making a scale model is enjoyable and needs technical expertise, accuracy, and creativity. Scale modeling lets you realize your designs in a physical form, whether you do it professionally or as a hobby. You can acquire the ability to make precise and intricate scale models by practicing frequently and adhering to the above-described procedures.
FAQs
A scale model is a physical representation of an object that maintains accurate proportions but is reduced or enlarged in size. It’s commonly used in architecture, engineering, film, and hobby design to visualize concepts before full-scale production.
The most common types include:
-
Architectural models (interior/exterior structures)
-
Engineering models (machines or industrial setups)
-
Miniature models (used in games, dioramas, or collections)
-
3D printed models (digitally designed and physically printed)
Each serves different purposes based on detail, scale, and functionality.
The right scale depends on the purpose and available space. Common architectural scales include 1:50, 1:100, or 1:200. For hobby models or collectibles, scales like 1:12, 1:24, and 1:72 are popular. Always consider the level of detail needed and how large or small the final model should be.
Typical materials include foam board, plastic, wood, metal, cardboard, clay, and 3D printing resin. The choice depends on the model’s complexity, durability requirements, and desired finish. Tools like cutting knives, glue, paint, and modeling kits are essential for the build process.