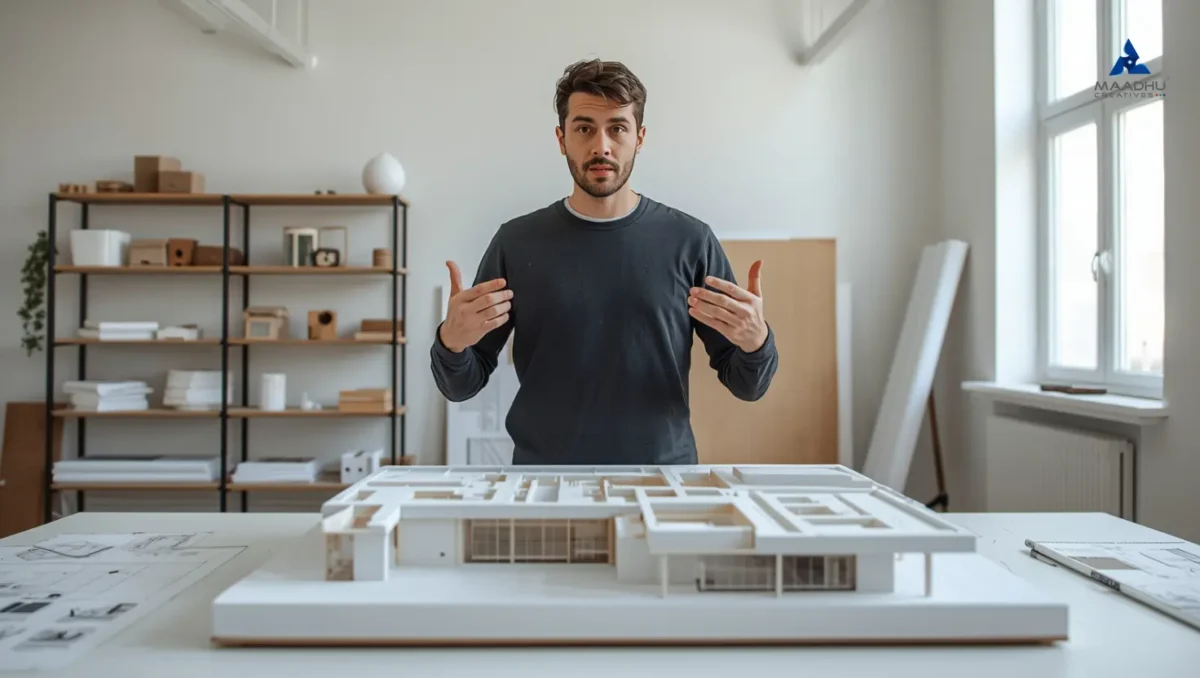
How Concept Models Turn Ideas Into Reality: Everything You Need to Know
Table of Contents
Introduction
Concept models play an essential role in turning abstract concepts into concrete representations. They can be used in design, engineering, architectural design, or in product development, conceptual models assist designers to visualize potential as well as identify problems early and convey ideas with precision. In the field of modeling these models are the basis to refine ideas and guide development teams to achieve successful results.
This thorough guide will explain the roots of concept modeling, its significance and the various types of processes and practical applications. If you are involved in the field of architectural model making or 3D model creation, prototype development or miniature building This blog will teach you all you need to know about.
The History of Concept Models
Concept models have been in use for hundreds of years. The earliest civilizations used physical models to show landscapes, structures and ideas well before the use of drawings in writing became popular.
In the past, in Egypt craftsmen constructed models of temples in the scale of houses and even boats to help plan building and convey concepts to the rulers. Similar practices were seen in the past in Greece and Rome in which architects constructed models of structures in miniature to investigate proportions and behavior.
In the Renaissance masters of art like Leonardo da Vinci frequently built models for prototypes to test the mechanical system such as flying machines and architectural concepts. The physical models enabled the innovators to evaluate feasibility well before the advent of modern technology.
In the age of industrial revolution the concept models were crucial for the development of machinery and products. Engineers made use of wooden and iron mockups to assess the functionality shape, fit, and. As technology advanced through the 20th century, architectural concept models were a common usage in urban planning and large-scale construction.
Today, thanks to the introduction of 3D printing, Digital visualization, 3D printing, and advanced materials, the concept of modeling is continuing to develop. However, its fundamental purpose is the same to provide clarity, direction and clarity from the beginning phases of designing.
What Are Concept Models
Concept models are the initial simple representations of a concept, form, or concept. Concept models allow engineers, designers and others to understand the form, function and spatial relations prior to the detailed development process begins. Concept models can be a useful beginning point to evaluate concepts, evaluating the proportions of concepts, and reworking ideas.
Modern concept model making involves an amalgamation of physical conceptual model, 3D concept models, and digital visualization. The models allow teams to communicate concepts with a high degree of accuracy and help reduce expensive revisions later on in the development process.
Why Concept Models Matter in Design and Development
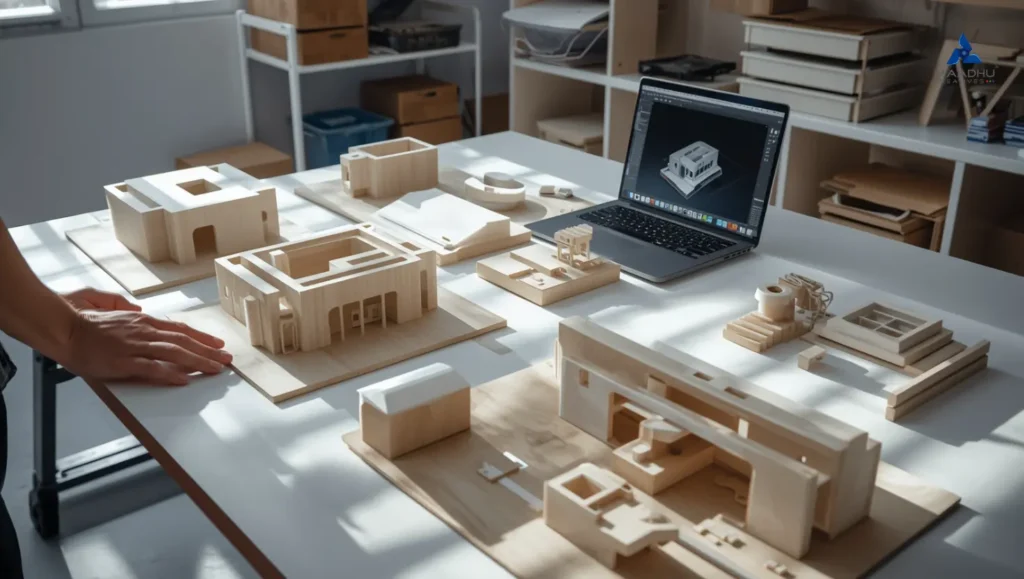

Concept models are employed for their unique advantages during the design phase. Here are the primary benefits of them:
1. Clear Visualization
Ideas for design usually start with abstract ideas. Concept models transform these ideas into tangible or 3D. They can be made by scale models or 3D model making. They aid teams in understanding the form, dimensions and function of a concept more clearly than sketching it out on paper.
2. Early Problem Detection
Concept models enable designers to detect flaws or shortcomings prior to proceeding to more detailed design. Recognizing issues early can save significant time and money, particularly when designing engineering concepts and prototype designs.
3. Better Communication
Physical concept models, or an expertly constructed miniature aids all stakeholders to be able to comprehend the design quickly. This is essential for engineering, architecture, and development of products, where many teams must work together and make well-informed decisions.
4. Enhanced Decision Making
The process of creating a conceptual model encourages the exploration of different options. Teams are able to compare various forms as well as materials and functions before deciding on a direction. This increases creativity, precision and performance of the product.
Types of Concept Models
There are many types of concept models, based on industry, purpose, and design stage. Here are the most commonly used and most widely used models:
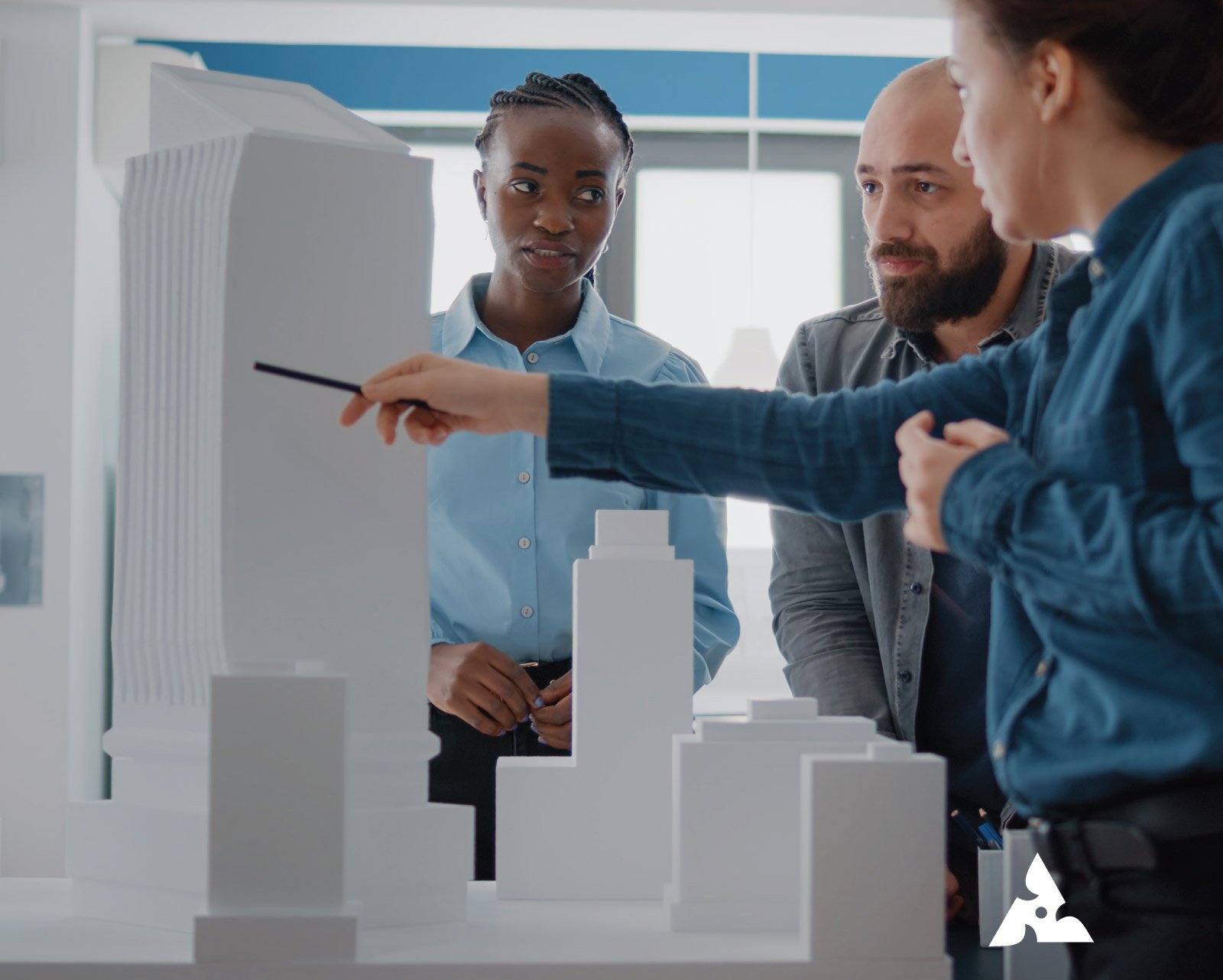
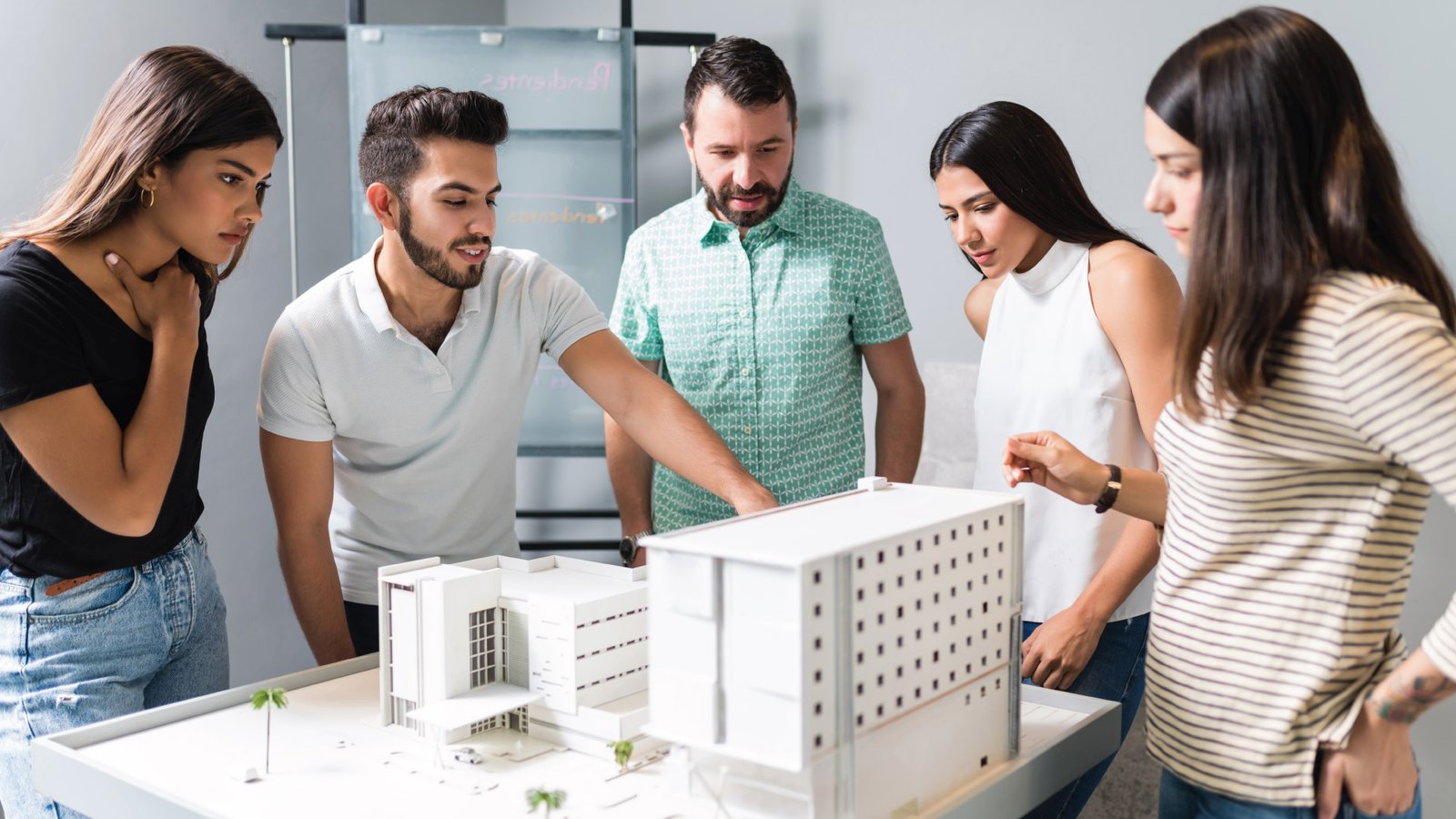
Physical Concept Models
Physical concept models are made by hand or machine-created miniatures that show the structure and form of an idea. These models allow teams to feel, study, and assess physical features more effectively than sketches.
They are used extensively in the fields of architecture, urban design and prototyping products. Commonly, they are made of foam board as well as wood, acrylic, 3D-printed materials, and resin.
3D Concept Models
3D Concept designs are representations of digital images that are created by using CAD software. They enable designers to move, scale and test forms quickly. These models are particularly helpful to test technical aspects such as interaction, movement and mechanical behaviour.
Architectural Concept Models
Architectural concept models concentrate upon spatial arrangements, masses, visual composition, and textures. They aid architects in understanding the spatial flow of spaces and the relation between buildings, as well as the effects of shadows and light. They play an important function in presenting concepts to planners and developers.
Engineering Concept Models
Engineering concept models study the capabilities and performance of the design. They assist teams to understand the mechanical behaviour as well as structural integrity and the interactions between components. These models are necessary prior to developing a functional prototype.
Prototype Models
Prototype models function as functional or semi-functional variants of designs. They verify how a design can function in actual situations. Industries like automotive, consumer electronics and industrial equipment depend heavily on prototype models to test the usability as well as technical efficiency.
Industrial Concept Models
Industrial Concept models study the design, ergonomics, and the interaction with users of the product. These models aid in assessing the way a consumer will hold, interact with, or feel the product prior to it entering production.
Where Concept Models Are Used
Concept modeling is used across many industries. Here are the most important industries in which it plays an important function:
Architecture
Concept models of architecture are necessary to understand massing, form and spatial connections. They aid architects in assessing the size of structures, the arrangement of rooms, as well as the interplay between buildings and their environments.
These models facilitate collaboration in design discussions, presentations to clients and also approvals from the planning authorities. They can be created by the process of architectural model making or 3D model creation. They are the foundation of architectural decisions made in the early stages.
Product Design
In the design of products, concept models assist teams to understand the ergonomics, shape and usability of the product. Concept models that are physical allow designers to understand how a product will fit in the hands as well as how it moves and how people use it.
Industries like medical devices, consumer electronics and household appliances rely on the concept of modeling products to improve ideas prior to production.
Engineering
Engineering Concept models aid in evaluating mechanical and structural properties prior to creating large-scale systems. The models concentrate on how the components interact, move, and can withstand stress or pressure.
They are extensively used in the design of machinery, robotics automobile systems, as well as aerospace engineering.
Manufacturing and Industrial Development
Scale model creation and conceptual models for industrial applications aid in the development of machinery, tools and equipment. They help manufacturers test the capabilities for their items, assess the performance of their products, and increase efficiency.
The Concept Model Development Process
Concept models are created through a variety of stages. This is how it happens generally works:
1. Research and Idea Exploration
The process starts by looking up the requirements of users along with the technical specifications and standards of industry. Teams look over references, assess competitors, then set objectives.
2. Sketching and Initial Concepts
Sketches are a great way to visualize the initial concepts. A variety of options are offered to study the shape as well as the function, and also the viability.
3. Material Selection
The modeling company selects its materials based on the purpose of usage of the design. Clay, foam, acrylic paper, cardboard, and 3D printing materials are the most commonly used materials.
4. Creating the Model
Creating your model is the next step in this process. A model maker will be concerned with the scale and clearness of your model, as well as how accurately your model has been made. Designers that create digital models typically use CAD (computer-aided design) software and 3D (three-dimensional) models.
5. Testing and Evaluation
The teams review the model to identify improvements that can be made. The primary focus is on aesthetics, usability, mechanical performance, and spatial flow, based on the model’s type.
6. Refinement
Based on feedback from the users, Designers modify the concept and alter the details, and finally decide the direction to follow in the next design phase.
Conclusion
Concept models are a vital element of modern development and design. They offer clarity, precision and direction in the beginning of the development. If you’re involved in modeling for architectural purposes, 3D model making, engineering or industrial design, conceptual models assist in transforming ideas into tangible and well-planned outcomes. Their lengthy history and continual significance demonstrate their value in the creative and technical fields.
A solid conceptual model guarantees that projects begin with clarity, move forward efficiently, and reach the goal with certainty.
FAQs
Concept models allow you to conceptualize ideas, pinpoint design problems, and help effectively communicate ideas across teams and customers.
Common products include foam board wood, acrylic, cardboard clay, resin as well as 3D printer filaments.
Both serve distinct purposes. Digital models permit the rapid exploration of ideas, whereas physical models give a real perception of scale, form and realism.