How to Design a Professional 3D Printing Model
Table of Contents
Introduction
3D printing has grown to be an increasingly important technology in the current manufacturing, engineering as well as creative fields. What began as an experiment in prototyping methods in the 1980s has evolved into a major production tool that is used in medicine, architecture automotives, aerospace and consumer products, fashion and even digital manufacturing. Making an effective 3D printer today demands much more than simply making a digital model on screen. It requires technical expertise of engineering logic, the knowledge of materials science as well as an understanding of how each printing technology performs in real life.
If you’re working using a 3D printing service, experimenting with the possibility of custom 3D printing options, or working with professional 3D printing firms like Maadhu Creatives, the digital model is the basis of the final product. In the event that your model has been created correctly printing will be seamless and precise as well as affordable. If the model is created poorly, even the top printing machines will not be able to save it. This comprehensive guide will help you comprehend the background, function and process of design required to make an expert 3D printing model suitable to any modern technology, including SLA, DLP, FDM, SLS, MJF, PolyJet, DMLS, and binder jetting.
A Brief History of 3D Printing
The development of 3D printing started in 1983, when stereolithography was made available. The first stereolithography machine utilized ultraviolet light to melt the resin layer by layer. This innovation was the first technique that was successful in creating 3D objects using digital data. While the first machines were costly as well as slow to operate, these machines were the start of an entirely new age of manufacturing.
In the coming 20 years, new technologies were introduced including:
- FDM melts plastic filament and then extrudes it
- SLS makes use of lasers to fuse powdered materials
- SLA and DLP are resin parts that produce extremely detail-oriented resin parts
- Binder jetting, which produces ceramic, sand, and metal shapes
- DMLS is a printer that prints sturdy metal components
- PolyJet and Material Jetting that allow multi-color and multi-material printing
These breakthroughs made it possible to create quick prototypes, small-scale products, custom-designed items, creative models, engineering parts as well as functional parts for end-of-life use. Today, top 3D printing firms, including Maadhu Creatives use advanced machines including SLA 3D printers, DLP equipment, SLS machines, MJF printers, PolyJet systems, DMLS metal printers, and industrial binder jetting systems that create accurate, long-lasting and visually stunning models for the industries of the globe.
Purpose of a Professional 3D Printing Model
A professional 3D printing model is designed with accuracy, intention, and engineering logic. The purpose of such a model is to ensure the final printed result is:
- Accurate to its dimensions
- Structurally strong
- Free of errors
- Visually clean
- Fully printable without issues
- Aligned with the selected 3D printing technology
A high quality model reduces cost, prevents failed prints, avoids structural deformities, speeds up production, and eliminates unnecessary post processing. Whether you choose 3D print on demand or rely on a full 3D printing service, your digital model determines everything.
Professionally designed digital models:
- Maintain correct thickness and geometry
- Keep structural stability in every area
- Deliver precise and sharp details
- Fit together perfectly in assemblies
- Use materials efficiently
- Reduce sanding and finishing time
This is why expert design plays the most important role in creating professional 3D printed products.
Start with a clear vision and a Goal
Each successful 3D model starts with clarity. Before you open any software, determine the primary purpose of your model.
Do you ask yourself:
- Is it functional or is it purely decorative?
- It could be used as prototype, miniature model for presentation, or as a working mechanism
- What degree of detail is required?
- Do you require durability or flexibility? Or the finest details?
- Which material will work best for the application?
- Which 3D printing technique is the most suitable for you?
A clear set of objectives guides your design process and will aid in avoiding costly changes. When you know what the objective is your design can be efficient and precise.
Choose the Right 3D Printing Technology
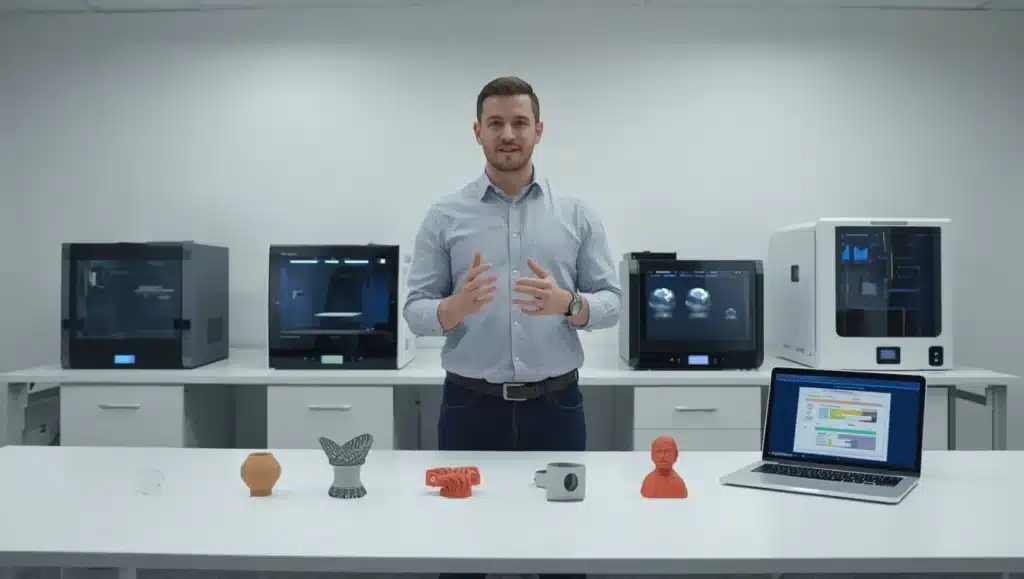

Each 3D printing technique comes with its own strengths. Selecting the best one will ensure that your final print is exactly as you would expect.
FDM 3D Printing
- Ideal for rough-prototypes
- Suitable for large models
- Cost effective
- It is great with simple shapes.
SLA 3D Printing
- Super smooth and precise
- Perfect for jewelry, miniatures, and parts that require precision
- High surface quality
DLP 3D Printing
- Faster resin printing
- Sharp and clear detailing
- The popular dental and miniature industries.
SLS 3D Printing
- High-strength
- No support structures are required
- Best for engineering components
MJF 3D Printing
- Accurate and strong
- Great for functional mechanical parts
- Perfect for production in batch
PolyJet and Material Jetting
- Multi-color and multi material capabilities
- Ultra fine surface finish
- Utilized in industrial and medical presentation
DMLS Metal Printing
- Metal parts that can be used in automotive and aerospace
- High durability
- Precision engineering quality
Binder Jetting
- Perfect for sand molds ceramics, and metal prints
- Quick and efficient
- For mass production
The correct choice of method guarantees the model performs flawlessly when printing and produces the desired result.
Apply Correct Wall Thickness
Wall thickness is a determinant of the strength in terms of durability, strength, and printing performance.
Guidelines for various procedures:
- FDM requires thick and strong walls to ensure the stability
- SLA and DLP have walls that are thin because resin is more precise.
- SLS and MJF provide uniformly thin walls, without putting yourself at the risk
- DMLS metal printing needs balanced walls to avoid deformation.
A wall that is not thick enough can cause warping, breaking or even complete failure of the print. Always ensure that you adhere to the recommended minimum thickness of the technology you choose.
Simplify and Refine Complex Details
Professional models are neat, well-organized, refined, and structured. The over-designing process can result in unfinished prints and unneeded complications.
The focus should be on:
- Smooth curves
- Balanced detail
- Sharp edges and clean lines
- Efficient geometry
- Transparent transitions between surfaces
Technologies like SLA, DLP, and PolyJet benefit most from subtle and thoughtful detail.
Use Correct Support and Model Orientation
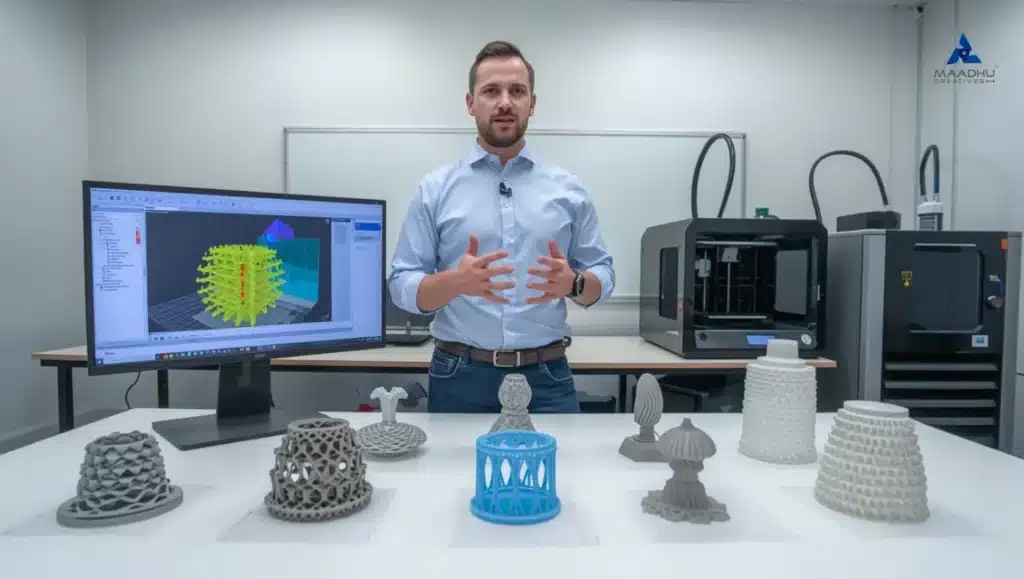

Model orientation plays a significant part in achieving professional results.
Correct orientation helps improve:
- Strength on the right line
- Surface smoothness
- Time to print efficiency
- Reduction of support structure
- Layer visibility
This is especially crucial for FDM, SLA, and DLP systems in which support layers or marks can alter the appearance of the system.
The design should be matched to the correct material
The selection of the materials will affect the performance and behavior of the final printed item.
Common materials are:
- PLA for low-cost prototypes
- ABS to be used for functional components
- Resin for detail-oriented high definition
- Nylon for engineering components
- TPU for flexible objects
- Metals for industrial applications
Select a material that is suitable for the environment of use and requires strength.
Add Tolerances and Clearances for Fitting Parts
If your design incorporates interlocking or moving components the need for tolerance is essential.
Include:
- A clear line between the mechanical joint
- Gaps to allow sliding and turning parts
- There is room for locking and hinge mechanisms as well as space to install the necessary hardware.
- A higher tolerance is required in resin printers that have shrinkage
A properly calibrated tolerance will ensure an assembly works seamlessly, with no melting or friction.
Validate the design by using Simulation Tools
Simulation helps verify your design before printing.
Simulations are a way to evaluate:
- Stress and load distribution
- Flexibility
- Shear resistance
- Balance of weight
- Twisting, bending and compression
This minimizes printing mistakes and enhances the final product, especially when printing engineering parts using SLS, MJF, or DMLS.
Prepare the File Properly Before Printing
A clean digital file will ensure the smoothest and error-free printing.
Final checks:
- Take away edges that are not manifold
- Close open surfaces
- Fix mesh holes
- Remove floating or hidden geometry
- Reduce the amount of polygons that are unnecessary
- Confirm the scale
- Export by using STL or OBJ and 3MF
A well-prepared file is crucial for any kind or type of 3D printing process.
Conclusion
Making an effective 3D printing model requires a lot of imagination and engineering expertise, as well as understanding of the material and a deep knowledge of the various printing technologies. It doesn’t matter if you’re using FDM, SLA, DLP, SLS, MJF, PolyJet DMLS, binder jetting, your 3D model determines the quality, reliability, and accuracy of the final printed item. With the proper planning, the correct wall thickness, precise details, optimized orientation, precise tolerance and the appropriate material selection, you can make professional models that function in a high-quality manner.
Companies such as Maadhu Creatives, known for their innovative 3D printing service and 3D printing services that are custom assist in bringing the digital design to life using precision, efficiency and high-end quality. When expert design principles are paired with the latest 3D printing technology the outcome is a flawlessly designed product that is ready for usage.
FAQs
SLA as well as DLP printing provide the best precision and quality of the surface and are ideal for jewelry, miniatures, and intricate components.
STL is the standard for industry, whereas OBJ 3MF and STL are great for advanced color models and details.
SLS, MJF, and DMLS offer exceptional strength and durability for engineering components.