Architectural Model Building: Materials, Accuracy, and Expert Techniques
Table of Contents
Introduction
The importance of visualization in modern architecture and design cannot be overlooked. Prior to erecting a single brick, architects and their clientele need to rely on complex models to visualize a project’s shape, proportion and relation to the surrounding space. Architectural modelling creates a physical medium to transform imaginative whiteness into a reality of expression.
An impressive architectural model emphasizes the integrity of the presentation, but it can also help with communication, reducing design errors, and establishing client trust. The use of digital tools, such as FreeCAD for architecture, Blender for architecture, and Rhino for architecture have created an unprecedented combination of craftsmanship and technology for model architecture.
This blog represents a starting point for everything you need to know about architectural model building: materials, accuracy, expertise, and how 3D architecture design and rendering services are changing the industry.
The Importance of Architectural Model Building
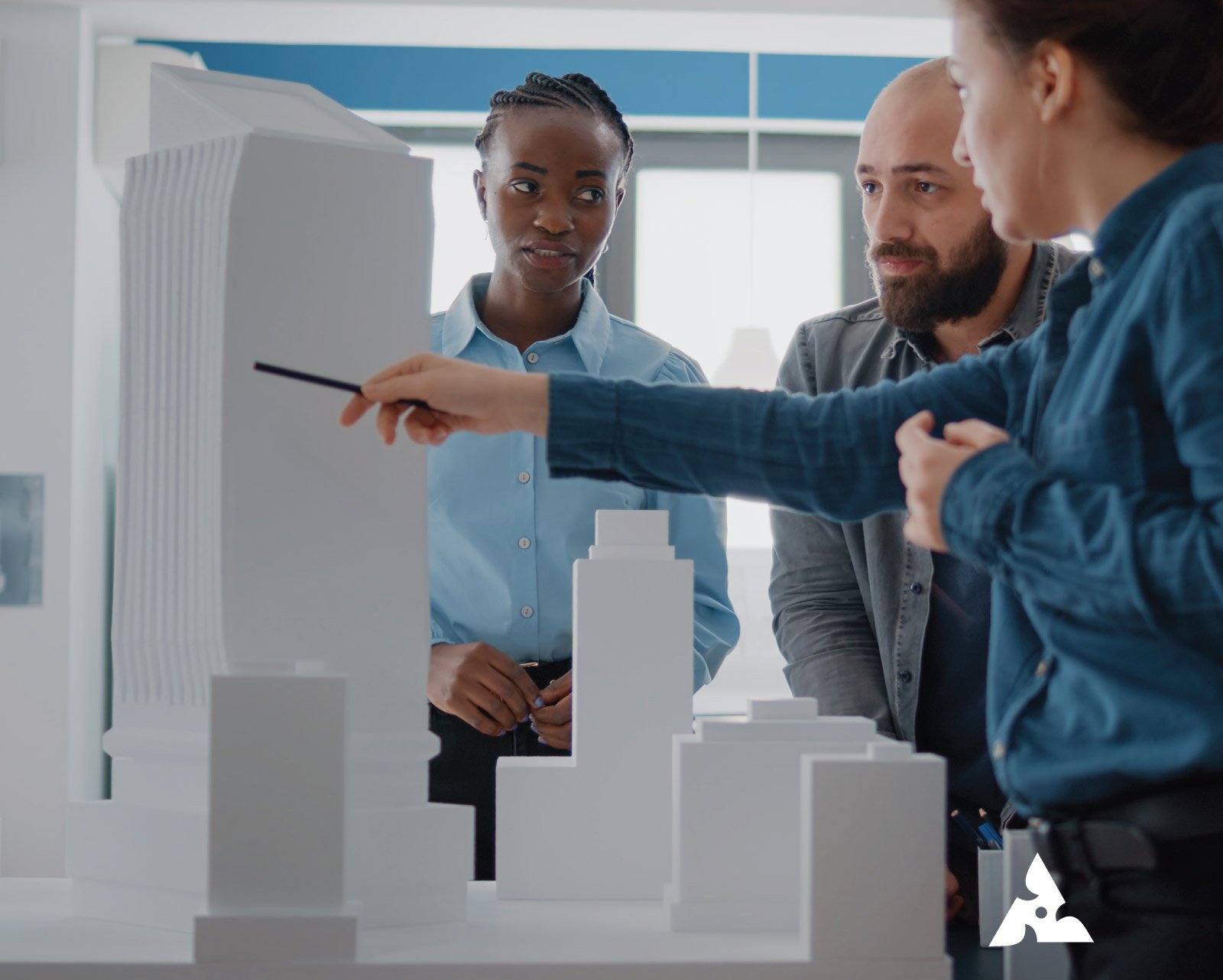
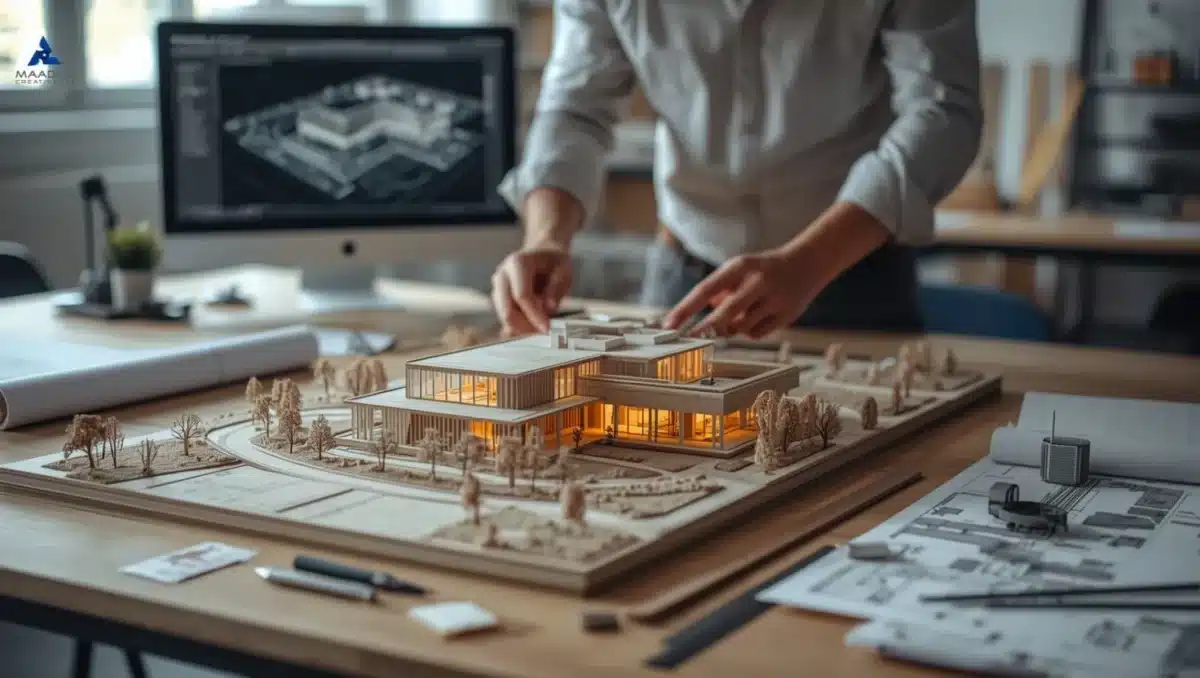
Architectural models are essential tools in all aspects of design and presentation. They give architects, engineers and clients an understanding of architecture in three dimensions, allowing for better-informed decisions. They also provide a physical experience in space that supports ideas in more of a tangible way than digital renderings can offer.
An architectural model is more than just a scaled down version of a building. It is a device to discuss space organization, design consideration, and material combinations. Whether used for developing design or for a client presentation, and regardless of complexity, an architectural model can engage stakeholders in a shared understanding of the project.
Combining traditional handcrafts with modern 3D architecture design ensures precision, realism and an element of professionalism at every step.
Types of Architectural Models

Conceptual Models
Conceptual models are developed early in the design process to test massing, configuration, and form. They are often made from basic materials such as foam boards, cardboard, or inexpensive wood products. Conceptual models are designed to be a way to brainstorm and clarify architectural design ideas before venturing into a more detailed design process.
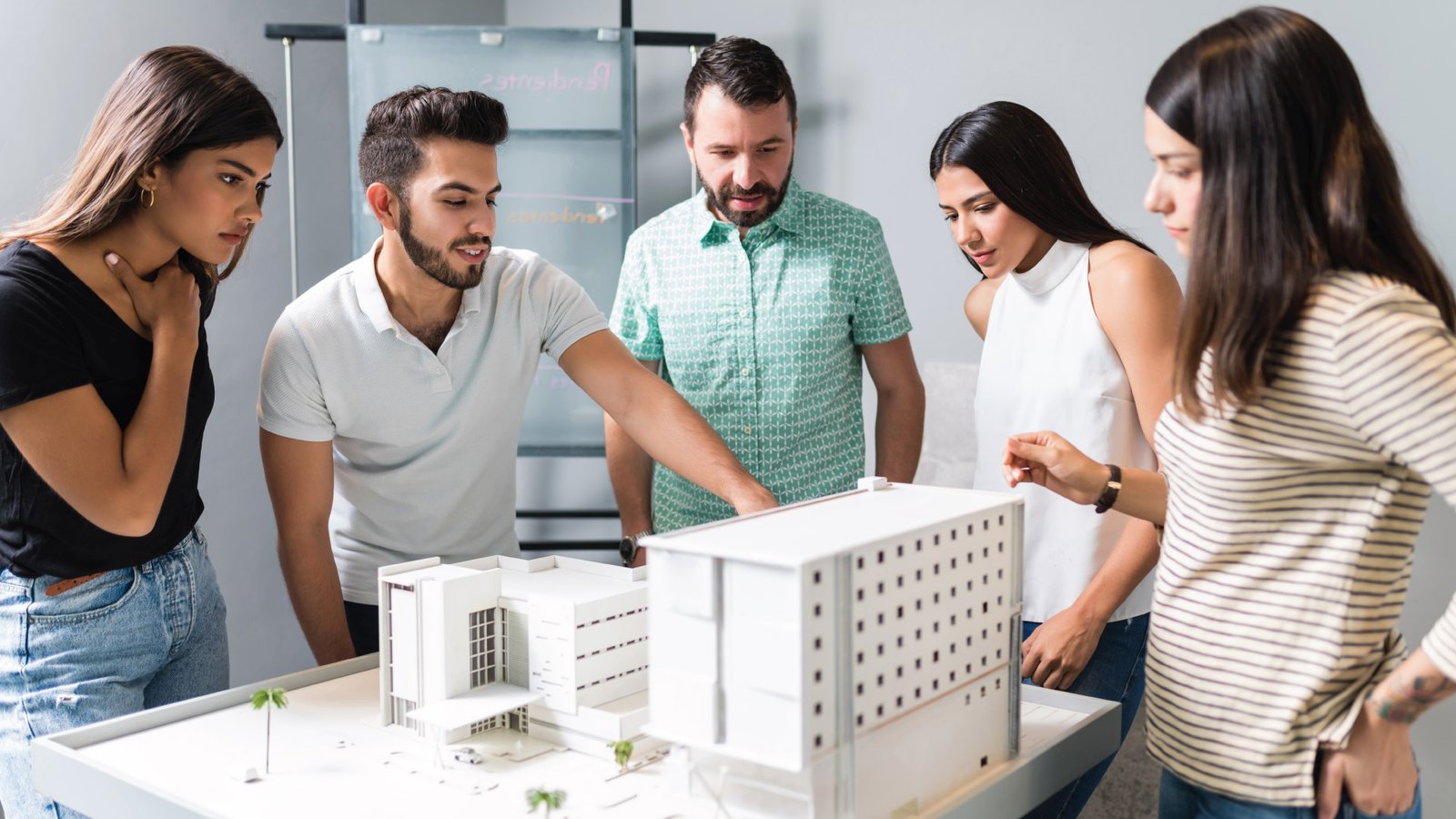
Presentation Models
Presentation models can provide visually-rich detail and tend to wow clients and/or investors. They usually feature realistic textures, interior configuration, and landscaping. When presentation models are bundled with 3D architectural rendering, an amazing visual for the final project is possible.
Working Models
Working models are functional models used by design consultants to test construction methodology, construction assembly, or structural reasons. Working models are more tied to accuracy and scale than aesthetically pleasing. Working models are extremely useful for technical evaluation and spatial exploration.
Landscape Models
An architecture landscape model also provides environmental context by presenting outdoor features, like gardens, roads, and existing buildings nearby. Landscape models can help clients conceptualize how the project will exist in the environment and help it fit with the landscape around it.
Digital 3D Models
With the help of digital design tools like Rhino for architecture, Blender for architecture, and FreeCAD for architecture, architects can create precise digital models that can later be 3D printed. These digital models enable realistic visualization and can be easily modified or shared for collaboration.
Materials Used in Architectural Model Making
Choosing suitable materials is essential in creating architectural scale models that are true to scale and aesthetically pleasing. All materials have unique characteristics to be employed, in most cases, during various stages of the model making process.
- Foam Board: very light in weight, and easy to cut, is a viable option for conceptual models.
- Cardboard: inexpensive for mock-ups and to establish structural ideas taken from the early phases of design.
- Acrylic Sheets: typically used in models for presentation purposes, have a quality finish that is both clear and sleek.
- Wood (Balsa or Basswood): a favorite for creating solid and true to scale architectural models that add realism and texture.
- Clay or Plaster: excellent when modeling organic shapes or when modeling landscapes.
- 3D Printed Materials: Well-liked to use for modeling is the modern age of 3D printed architecture with easy and complex components for precision.
The combination of forms of traditional materials and using digital fabrication methods such as laser cutting and 3D printing allows for a model to be more accurate and aesthetically pleasing in architectural scale model making.
Accuracy and Scale in Architectural Model Building
Precision is an essential aspect of architectural model making. Models will almost always be produced at a specific scale as in 1:50, 1:100, or 1:200 – maintaining some proportionate representation is key. A precision-scaled model would allow an architect to interpret dimensions, volumes, and spatial relationships.
New advances in digital tools, like FreeCAD for architecture and Rhino for architecture have improved the porcelain-type detail models that contain their form. The aforementioned programs also offer parametric design, so that when one aspect of a model changes, the change would be articulated and reflected across the entire model. We can not only express digital precision and detail but also handmade detail, of which professionals can produce technically accurate and visually beautiful architectural scale models.
Expert Techniques in Architectural Model Making
Creating a high-quality architectural model requires both creativity and technical expertise. Professional model makers use several techniques to ensure that every project looks realistic and functions as intended.
- Dividing to Create Layers and Sections: The designer finds that they can take complex designs and divide them into manageable elements. Division makes it easier to build the models and contributes to a more accurate end product.
- Applying Textures and Finishes: There are numerous ways to create finishes or textures- with paint, sandpaper, or applying a surface application that looks like wood, glass or metal.
- Incorporating Lighting: Including LED light strips adds depth and a sense of realism and interest to the interior 3D house design model.
- Digital Hybrid: Mixing a 3D print model with elements built by hand can create a happy medium between accuracy and creative exploration.
- Model Landscaping: The addition of vegetation, paths, and water elements provides realism for architecture landscape models.
These skills enhance the aesthetic and technical validity of the overall presentation of architectural models.
Benefits of Architectural Model Making
Architectural model making includes many benefits above and beyond aesthetic or presentation of the model.
- Improved Visualization: A model provides a greater understanding of the dimensions and scale.
- Communication Improvement: Physical models help share information from architect, to engineers and clients.
- Error elimination: Physical models establish a means to visualize design that could perhaps highlight possible errors in design before construction begins.
- Marketing Improvement: A professional model, or a 3D architecture rendering service, provides a visualization that is very powerful in client meetings and trade shows.
- Educational Value: Architectural models are excellent tools for teaching and training and can effectively depict and model principles and goals of design.
Combining the benefits of 3D architecture design and rendering technology, architects have greater accuracy in design, visual appeal for marketing and client meetings, and potential for attracting greater involvement from the client.
Digital Tools Enhancing Modern Architectural Model Building
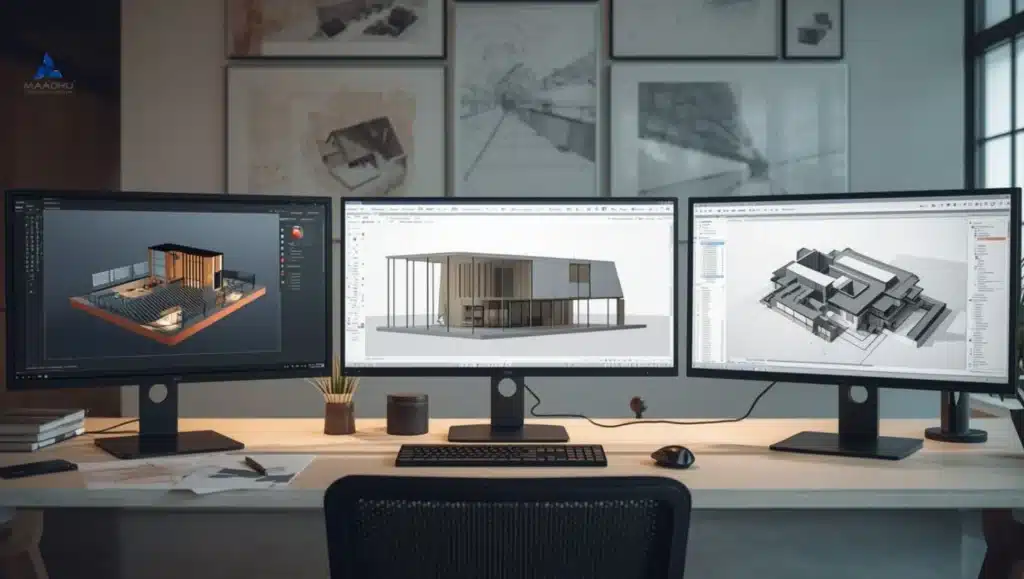

The development of digital tools has changed the ways architects design, plan, and present models.
- Blender for Architecture: Blender provides a digital tool that includes realistic 3D rendering, lighting simulation, and animation to present a very detailed visual model.
- FreeCAD for Architecture: FreeCAD is a digital tool for open-source parametric modeling for accurate development of design.
- Rhino for Architecture: Rhino is a specialized digital tool to model complex geometrical models and export for 3D printing.
These digital tools streamline workflows, allowing seamless integration between design visualization, architectural rendering, and physical model production.
Future Trends in Architectural Model Making
As technology has progressed, so too has the act and process of model making.These are trends that are likely to take place going forward:
- Augmented Reality Integration: The combination of physical models with augmented overlays provides much richer visualization of design.
- Sustainable Materials: Sustainable materials are expected to replace conventional plastics in many applications.
- Advanced opportunity in 3D Printing: The use of multi-material printing will afford models to be printed faster and with more detail.
- Interactive Models: Models that include movement, light, and/or sound are a way architects can present their arrangements in more engaging ways.
Each of these will progress to fundamentally change the way architects present and communicate design ideas to their client base.
Conclusion
Architectural model making is a unique mix of creativity, precision, and innovation. During each phase of model making, whether it is a form of conceptual sketching or 3D architecture design at a higher level, the architect needs skills, attention to detail, and tools of the trade to accomplish the desired intent of the model. The implementation of software such as Blender for architecture, Rhino for architecture, and FreeCAD for architecture may help architects achieve digital accuracy and physical accuracy.
Whether the purposes are a client presentation, project visualization, or educational, architectural model making remains one of the most powerful ways of expressing a vision of architecture! It transforms ideas into reality, bridging the gap between imagination and construction with craftsmanship, technology, and expertise.
FAQs
An architectural model serves the purpose of visualizing a project’s structure, scale, and plan prior to construction. This will help the architects and the client understand the overall design idea, allowing for improved communication and feedback during planning.
Utilizing tools, like Blender for architecture, FreeCAD for architecture, and Rhino for architecture, will support exact 3D modeling and rendering, improving accuracy through scale, dimensions, and detailing, thus the direct conversion into the physical architectural model.
Foam boards, acrylic sheets, and wood are some of the best materials used for architectural models. For more elaborate projects, however, models that are 3D printed are considered superior in precision and flexibility using numerous design details.
Architectural rendering is a digital representation showing lighting, materials, and textures. Meanwhile, architectural scale models are built with physical three-dimensional models. Renderings are used for online presentations whereas architectural models are a tactile architectural experience.