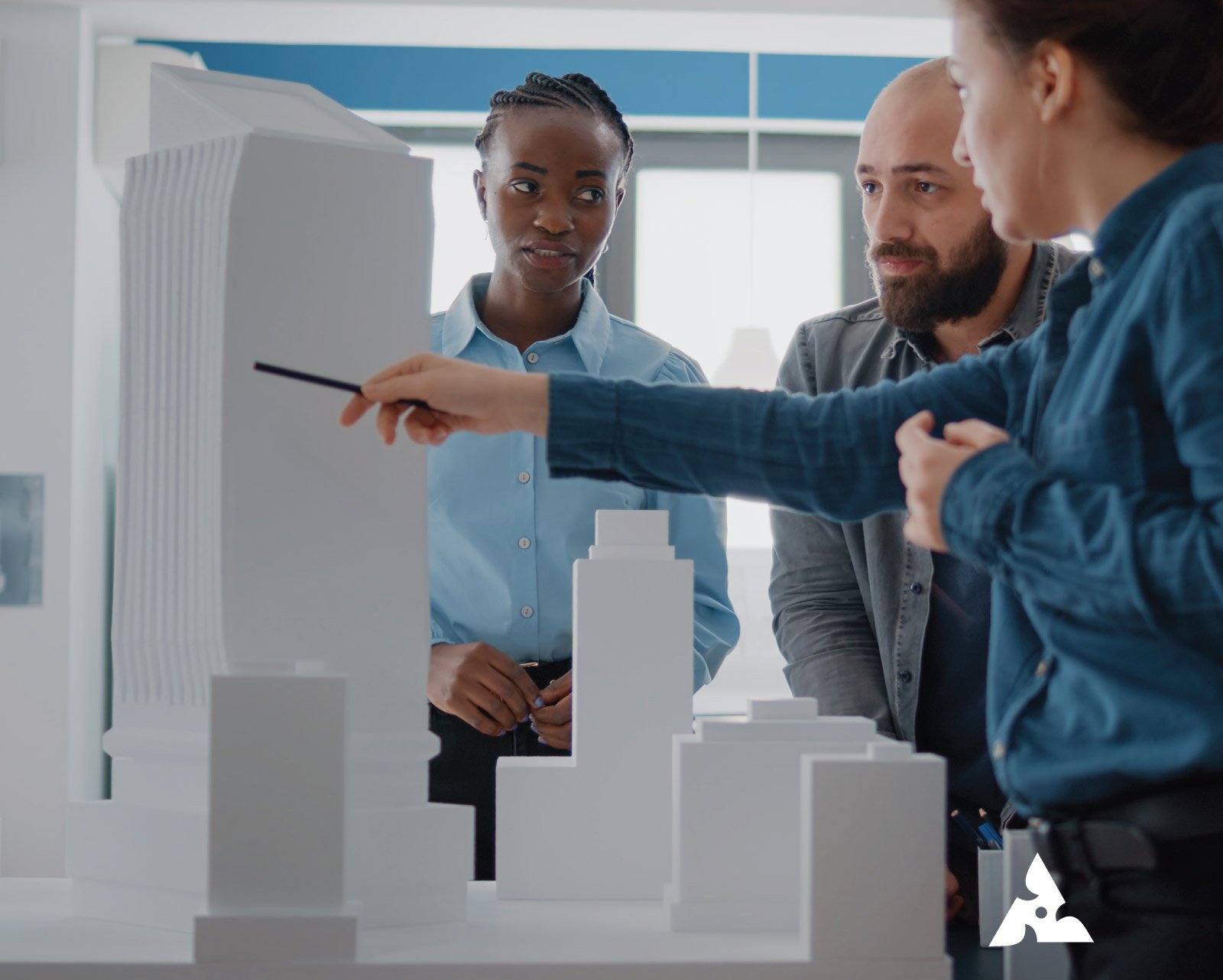
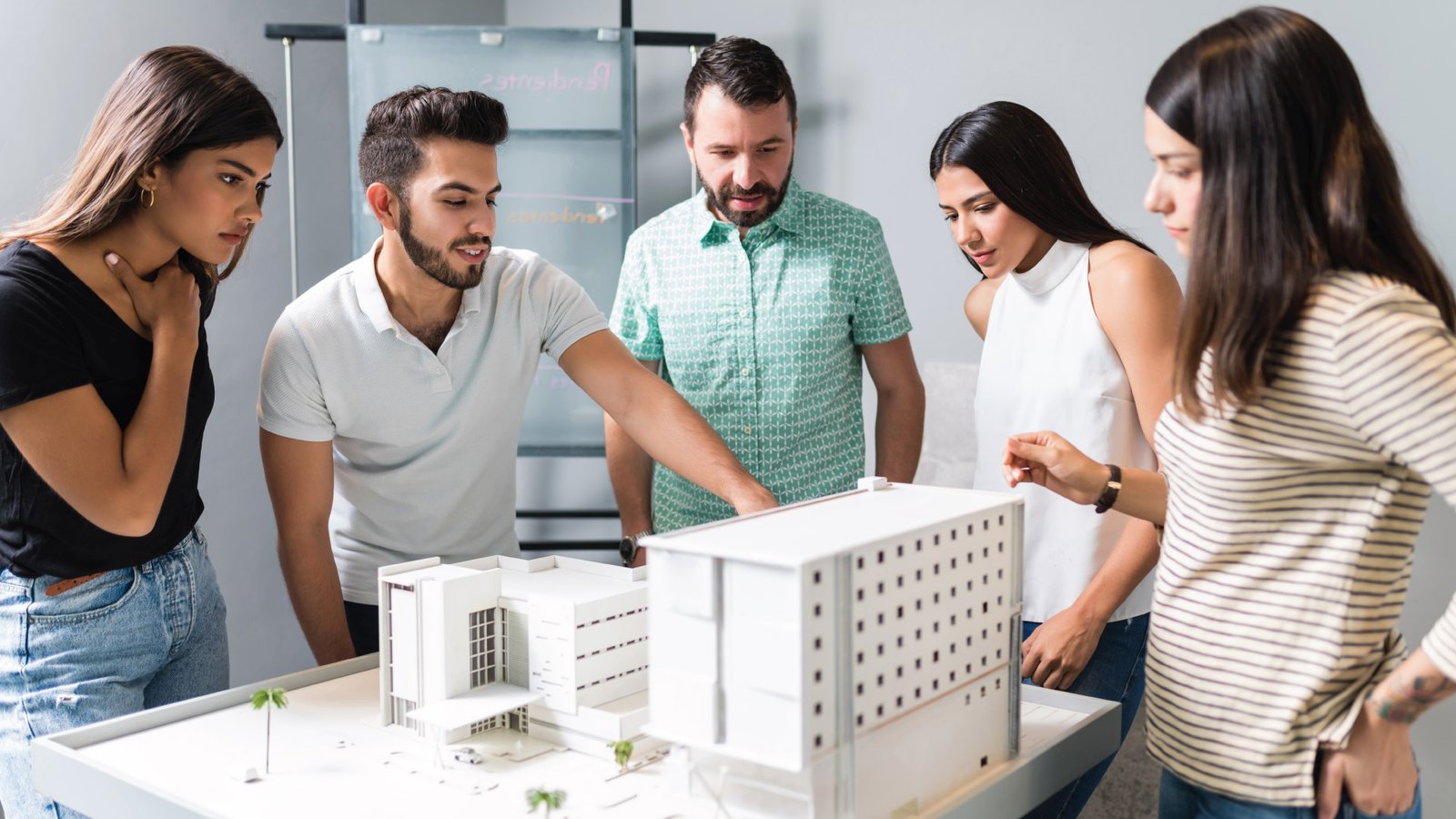
What Is 3D Visualization? A Simple Guide for Beginners Table of Contents Let’s Connect This is what 3D visualization is: the process of creating images, animations, or other interactive experiences to such an extent that objects, environments, or ideas are simulated as if they exist in a three-dimensional space. More importantly, it is depth in contrast to traditional 2D pictures or drawings. Moreover, it provides dimension. Today, its applications can be witnessed across many industries, whether in architecture, product design, animation, gaming, marketing, etc. 3D visualization basically serves as the main way of having easier explanation and interaction with complicated data, products, or even environments long before a product is developed. It delivers an immersion that shows things in such realistic forms and might be helpful for easy analysis and communication. This book will describe what 3D visualization is, how it works, and why it’s so powerful for both pros and amateurs. Through a look at the types of uses, how to get started, and the most common mistakes made by users, you will develop a well-rounded view of how 3D visualization plays in the creative world today. What Is 3D Visualization Service? A 3D visualization service refers to the professional creation of 3D models, images, and animations for a purpose, whether this is for presentation, marketing, or visualization in design. Professional services in 3D modeling, animation, and rendering using advanced software often relate to creating photorealistic or stylized digital representations of an object or scene. Services may include still images, 3D animations, and even interactive virtual or augmented reality experiences. Thus, an architectural firm may use this service of 3D visualization in order to present realistic renderings of a building design, allowing the clients to have an idea of space before it is built. Product designers use 3D visualizations to test and market prototypes, providing customers with a better idea of what the final product will be like and how it functions. This service is important in conveying ideas more effectively, improving decision-making, and reducing the risk of costly changes later in the design process. Types of 3D Visualization 3D Rendering: Rendering is the process of taking a 3D model and converting it into a real image or animation. This process involves adding details like textures, lighting, and shadows to the 3D model to make it look real. 3D rendering is commonly used in architecture, product design, and film production to show realistic images of designs or scenes. 3D Animation: 3D animation surpasses static images and brings designs to life. It involves creating a sequence of frames that show the movement of objects or characters in a 3D space. The type of visualization is mainly used in film, gaming, and product demonstrations to explain how a product or design will function in real life. Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) are interactive 3D visuals providing a more immersive experience, respectively. VR will immerse an environment in which users can interact with the 3D world using specific headsets. AR overlays 3D models onto the real world through a mobile device or AR glasses. These technologies have applications in gaming, educational environments, architecture, and marketing. 3D Modeling: This is the most primary step of creating a 3D visualization. In this, one designs a structure of an object or an environment using special software.It can then be rendered or animated or used in applications such as VR/AR. Modeling is the basis of all 3D visualization work for any 3D artist or designer. Top Tips for Getting Started with Visualization Start with a Clear Objective: What must come before 3D visualization is defining a clear purpose. One must ask one what s/he wants for the output of the visualizations in terms of getting a static image, an animated sequence, and perhaps a more interactive presentation. Such a purpose is necessary because it will let you make the right selection of software and approach as follows. Choose the Right Software: There are several 3D visualization software options. From simple, beginner-friendly applications like Blender to professional-grade tools such as Autodesk 3ds Max or Maya, the choice will depend on the user’s skill level and the requirements of the project. Most packages also have free versions or trial periods, allowing you to explore them before committing. Understand the Basics of Lighting and Texturing: Lighting and texturing are two of the key elements that bring a 3D scene to life. Lighting has a lot of effects on the mood and reality of your visuals, whereas textures give objects the look and feel of real-world materials such as wood, metal, or even fabric. Learn how to do proper lighting and textures to make your 3D models realistic. Practice and Experiment: As with every creative skill, 3D visualization is a process of acquiring mastery. You must start off with small projects and, based on your improvements, slowly build complexity into your work. Experimenting with various techniques, software settings, and design approaches won’t frighten you as long as you have seen it’s worth the time taken. Seek Feedback and Learn from Others: There is a massive community of 3D artists online, providing useful knowledge, tutorials, and advice. Make use of online forums, courses, and social media groups to learn from others and get feedback on your work. This will help avoid common mistakes and accelerate the learning process. Uses of 3D Visualization Architecture and Real Estate: Architectural companies use 3D visualization in order to create realistic renderings and walkthroughs of building designs. This way, the architects and clients can preview the project before it is actually built hence, changes may be easier to make and can easily meet the client’s requirements. In real estate, 3D visualizations are used for virtual tours and marketing purposes. Product Design and Manufacturing: 3D visualization helps designers create digital prototypes of products before manufacturing. In this way, they test their forms, functionalities, and ergonomics, thus helping identify issues early in the development process. The manufacturers can